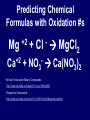* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Stability
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Ionic liquid wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Ionic compound wikipedia , lookup
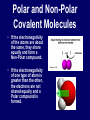
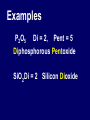
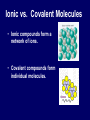
Chemical Stability Chemical Stability • All elements want chemical stability. • This can happen by: 1. Forming Ions 2. Forming chemical bonds (making compounds) Ion An atom (or group of atoms) that has lost or gained e- and has a net electric charge. – Cation (+) – Anion (-) Atom vs. Ion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dHZlMbBZ0UA What is an Ion? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=900dXBWgx3Y Valence Electrons • The number of electrons in the outer orbital of an atom. Ionization Atoms become ions in order to have a complete energy level. Fluorine Atom Fluorine Ion Ionization Oxygen atoms have 6 valence electrons Oxygen ions gain 2 e- and becomes O –2 Ionization Magnesium atoms have 2 valence electrons Magnesium ions lose 2 e- and become Mg +2 Oxidation Number The ion “charge”. Oxidation Numbers • Oxygen ion: O –2 [gained two e-] • Magnesium ion: Mg +2 [lost two e-] Electron Dot Diagrams Diagrams that display only the valence electrons Electron Dot Diagrams Atom Ion Mg loses 2e- Mg+2 N gains 3e- N -3 Li loses 1e- Li +1 Polyatomic Ions A group of atoms with a net charge. OH -1 NO3 -1 PO4 -3 CO3 -2 Polyatomic Ions How to Remember Certain Common Polyatomic Ions Nick the Camel ate a Clam for Supper in Phoenix http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jcKR9U4Ixlk Compounds • Two or more elements chemically bonded to form a new substance (with different properties). Compounds • Shown by: – Chemical Formula H2O – Structural Formula O H H Compounds • Chemical Formula Coefficient 3H2O (# of Molecules) Subscript (# of atoms) Parentheses (OH)2 = chemical groups Compounds • Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas 3H2O Compounds • Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas 6CO2 4NaHCO3 3H3PO4 5Mg(OH)2 2Fe3Al2(SiO4)3 Chemical Bonding • Chemical Bonding occurs to achieve Chemical Stability. • Atoms gain, lose or share valence electrons. Why do Atoms Bond? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JOL-nUt_vfo&feature=youtu.be&app=desktop Bonding Song http://gaygeek.com.au/blog/2012/09/19/atomic-bonding-love-song-video/ Types of Bonds • Ionic • Covalent • Metallic The Type of Bonding Depends on the Difference in the Electronegativity of the Atoms. Ionic Non-Polar Covalent Polar Covalent Ionic Bonds • Bonds formed by the attraction between oppositely charged ions. [e- are given away or received] Ionic Bonding http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xTx_DWboEVs Ionic Bonding Rules: 1) Metals form ionic bonds with nonmetals. 2) Metal form ionic bonds with polyatomic ions. 3) Polyatomic ions form ionic bonds with each other. Ionic Bonding Lewis Dot Diagrams show chemical bonds resulting from interaction of valence e- and the ion charges. _ - +3 - Predicting Chemical Formulas with Oxidation #s Mg +2 Ca +2 + Cl MgCl2 - + NO3 Ca(NO3)2 - Writing Formulas for Binary Compounds http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vscoYh6m46M Polyatomic Compounds http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3K5V3kxxlI8&feature=related Naming Ionic Compounds • Names are additions of cations and anions • Cation (1st) is usually the name of the element. • Anion (next) is the 1st syllable of the element PLUS the suffix “ide” Examples: Li and F = Lithium Fluoride Mn and O = Manganese Oxide Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic Ions Name the Cation, then the Polyatomic Ion. Ca+2 + (CO3-2 ) ions = Calcium Carbonate Na+ + (CN- ) ions = Sodium Cyanide Ba+2 + (SO3-2) ions = Barium Sulfite Covalent Bonds • Bonds formed by sharing electrons. Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QqjcCvzWwww Covalent Bonding http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j1e-f1W-0UA Covalent Bonding Rules: 1) Hydrogen forms covalent bonds with metals, non-metals and polyatomic ions. 2) Nonmetals form covalent bonds with other nonmetals. Covalent Bonds in EDD Diatomic Molecules Some atoms, (mainly gases) share their extra electrons. Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Molecules • If the electronegativity of the atoms are about the same, they share equally and form a Non-Polar compound. • If the electronegativity of one type of atom is greater than the other, the electrons are not shared equally and a Polar compound is formed. Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Molecules Naming Covalent Compounds • Covalent Compounds are molecules (not ions) bonded together. • Name reflects the numbers of each element in the compound. • Use Latin prefixes. Latin Prefixes • • • • • • • One (1): Mono Two (2): Di Three (3): Tri Four (4): Tetra or Tetr Five (5): Pent or Penta Six (6): Hex or Hexa Seven (7): Hept or Hepta Examples P2O5 Di = 2, Pent = 5 Diphosphorous Pentoxide SiO2 Di = 2 Silicon Dioxide There’s always an Exception • If the first letter of the atom is a vowel, drop the “a”. • Examples: – Dinitrogen Tetroxide – Carbon Tetrafluoride Ionic vs. Covalent Molecules • Ionic compounds form a network of ions. • Covalent compounds form individual molecules. Ionic vs. Covalent Molecules Properties of Ionic Compounds • • • • High Melting / Boiling Points Brittle Many are Water Soluble When dissolved in water, conduct electricity because they are charged particles [Electrolytes]. Properties of Ionic Compounds http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c546LZPgYwA&safe=active http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kgiwdaVMax8&safe=active How water Dissolves Salt http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xdedxfhcpWo Ionic vs. Covalent Molecules Properties of Covalent Compounds • • • • Low Melting / Boiling Points Usually Liquid or Gas “Like Dissolves Like” Since they are neutral molecules, they do not conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Properties of Covalent Molecules http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OQ-pcxo-Q5c&safe=active Like Dissolves Like http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7OuJ6ierB9s&safe=active