* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Maths Workshop - St Michael`s C of E Primary School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
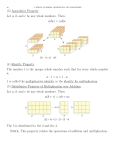
Efficient written methods for calculating addition, subtraction, multiplication and division by the end of year 6. Partition into tens and units and recombine 12 +15 + 21 = 12 = 10 + 2 15 = 10 + 5 21 = 20 + 1 Recombine 10 + 10 + 20 =40 2 + 5 + 1 = 8, 40+ 8 = 48 Partition into tens and units and recombine 12 +15 + 21 = 36 + 42 = Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain addition and subtraction. 227 + 312 = ? 200 20 300 10 500 + 30 + 7 2 9 = 539 Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain addition 36 + 42 = 227 + 312 = 227 + 315 = Using a standard written method 227 + 315 = Most significant digits first 227 + 315 500 030 012 542 Least significant digits first 227 + 315 012 030 500 542 Prepares for carrying + 227 315 542 1 Using a standard written method 227 + 315 = 4567 + 315 = Using a standard written method; carrying 4567 + 315 = 4567 + 315 4882 1 421.36 + 25.7 = 421.36 + 25.70 447.06 1 Using a standard written method; carrying 4567 + 315 = 421.36 + 25.7 = Counting up from the smaller to larger number (complementary addition) 84 – 56 = 56 + 4 + 20 + 4 = 84 +20 +4 84 - +4 56 4 to 60 20 to 80 60 56 4 to 84 80 84 28 Begin to record calculations in preparation for an efficient standard method; decomposition 84 – 56 = 84 - 56 4 to 60 20 to 80 4 to 84 28 Apply partitioning skills - 84 = 80 + 4 = 70 + 14 56 50 + 6 = 50 + 6 20 + 8 = 28 Counting up from the smaller to larger number (complementary addition) 46 – 25 = 84 – 52 = 84 – 56 = Begin to record calculations in preparation for an efficient standard method; decomposition 46 – 25 = 84 – 52 = 84 – 56 = Record calculations in preparation for an efficient standard method; decomposition No decomposition 89 = 80 + 9 - 57 50 + 7 30 + 2 = 32 Decomposition 81 = 80 + 1 = 70 + 11 - 57 50 + 7 = 50 + 7 20 + 4 = 24 Record calculations in preparation for an efficient standard method; decomposition 89 – 57 = 84 – 57 = 284 – 57 = Continue to develop an efficient standard method; decomposition - 754 = 700 + 50 + 4 286 200 + 80 + 6 leading to 1 = 700 + 40 + 14 744 6 - 286 6 14 14 = 600 +140 + 14 11 644 754 200 + 80 + 200 + 80 + 6 400 + 60 + 8 - 286 -286 468 468 Continue to develop an efficient standard method; decomposition 754 – 286 = 5821 – 764 = 4567 – 893 = Develop and use an efficient standard written method; decomposition 5 13 16 3 16 6467 - 2684 3783 12467 - 84 12383 Develop and use an efficient standard written method; decomposition 6467 – 2684 = 782 175 – 4387 = 324.9 – 7.25 = Understand multiplication as repeated addition and as an array. (rows are always mentioned before columns) 3 rows of 5 = 15 5 3 x 5 = 15 5 + 5 + 5 = 15 5 rows of 3 = 15 5 x 3 = 15 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 15 3 Modelling the number properties involving multiplication using an array of objects not only allows children to represent their thinking with concrete materials, but it can also assist the children to form useful mental pictures to support memory and reasoning. Commutative property The commutative property of multiplication can be neatly illustrated using an array. For example, the array above could be read as 2 rows of 6, or as 6 columns of 2. Or the array could be physically turned around to show that 2 rows of 6 has the same number as 6 rows of 2. Regardless of the way you look at it, there remain 12 objects. Therefore, the array illustrates that 2 x 6 = 6 x 2, which is an example of the commutative property for multiplication. Being able to apply the commutative property means that the number of multiplication facts that have to be memorised is halved. Understand multiplication as repeated addition and as an array. 4x3= 6x3= 5x6= Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain multiplication. 23 x 3 23 x 3 = (20 x 3) + (3 x 3) Grid method Times tables x Partitioning Array 3 20 3 60 9 = 69 Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain multiplication 12 x 9 = 26 x 3 = 35 x 16 = Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain multiplication Grid method 346 x 9 x 9 300 40 2700 360 6 54 2700 = 360 + 54 3114 Continue to develop an efficient standard written method Short multiplication 346 x 9 346 x 9 300 x 9 2700 40 x 9 360 6x9 54 3114 leading to 346 9 x 3114 45 Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain multiplication Grid method 346 x 9 Develop an efficient standard written method Short multiplication 543 x 7 Continue to develop an efficient standard written method Long multiplication 72 x 38 72 x 30 2160 72 x 8 576 2736 72 x 38 Continue to develop an efficient standard written method Long multiplication 72 x 38 Chunking! Division made easy! Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain divisions 42 ÷ 3 = ? 10 groups of 3 4 groups of 3 Chunks –12 –-30 - 30 - 12 0 0 12 12 10 chunks + 4 chunks = 14 42 Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain divisions 21 ÷ 3 42 ÷ 3 54 ÷ 6 Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain division Using multiples of the divisor (CHUNKING) 72 72 ÷ 5 - 50 10 x 5 22 - 20 4x5 2 Answer: 14 remainder 2 Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain division 72 ÷ 3 = 72 ÷ 4 = 72 ÷ 5 = Develop an efficient standard written method Short division 196 ÷ 6 32 R 4 6 ) 196 18 (30 x 6 = 180) 16 12 4 (2 x 6 = 12) (remainder) Develop an efficient standard written method Short division 196 ÷ 6 256 ÷ 7 Continue to develop an efficient standard written method Short division (thousands) 2196 ÷ 6 366 6 ) 2196 1800 (300 x 6 = 1800) 396 360 36 (60 x 6 = 360) (6 x 6= 36) Continue to develop an efficient standard written method Short division (Bus Stop Method!) 366 6 233 ) 2196 6 into 2 doesn’t go – carry the 2 over. 6 into 21 goes 3 remainder 3 – carry the 3 over. 6 into 39 goes 6 remainder 3 – carry the 3 over. 6 into 36 goes 6 exactly. 2196 divided by 6 = 366! 2196 ÷ 6 Continue to develop an efficient standard written method Short division (thousands) 2196 ÷ 6 4321 ÷ 6 8104 ÷ 6 Know what each digit represents and partition three-digit numbers into a multiple of 100, a multiple of 10, and ones. Understand multiplication as repeated addition and as an array. Add three two-digit numbers using apparatus or informal methods. Partition into tens and units and recombine. Add or subtract a near multiple of 10 to a two-digit number, by adding or subtracting the nearest multiple of 10, and adjusting. Choose appropriate number operations and calculation methods to solve word problems. What is partitioning? Know what each digit represents and partition three-digit numbers into a multiple of 100, a multiple of 10, and ones. 243 3 200 40 What is an array? Understand multiplication as repeated addition and as an array. 3 x 5 = 15 5 + 5 + 5 = 15 3 5 What does it mean by informal method? Add three two-digit numbers using apparatus or informal methods. 12 +15 + 21 = + 20 +7 41 21 48 10 + 10 + 20 =40 2 + 5 + 1 = 8, 40+ 8 = 48 Why is partitioning so useful? Partition into tens and units and recombine. 12 +15 + 21 = 10 + 10 + 20 =40 2 + 5 + 1 = 8, 40+ 8 = 48 It’s one of those informal methods! What does it mean by adjusting Add or subtract a near multiple of 10 to a two-digit number, by adding or subtracting the nearest multiple of 10, and adjusting. 39 + 34 = ? 40 + 34 = 74 Round up 39 to 40 40 + 30 = 70 Partitioning 70 + 4 = 74 74 – 1 = 73 Recombine A clearly written answer To add/subtract by counting on or back in repeated steps of 1, 10, 100. Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain addition and subtraction. Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain multiplication. Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain divisions. Choose appropriate number operations and calculation methods to solve word problems. What is counting on and back on a number line? To add/subtract by counting on or back in repeated steps of 1, 10, 100. 227 + 300 + 100 + 100 337 227 + 100 437 537 What does it mean by informal method? Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain addition and subtraction. 227 + 312 = ? 200 20 300 10 500 + 30 + 7 2 9 = 539 What does it mean by informal method? Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain addition and subtraction. £5.20 - £3.60 = ? Demonstrate the need to re-partition the numbers as: £5.20 - £3.60 = £4 + 120p subtract £3 + 60p = £4 - £3 and 120p – 60p = £1 and 60p = £1.60 What another informal method? Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain multiplication. 23 x 3 23 x 3 = (20 x 3) + (3 x 3) Times tables x Partitioning 3 20 3 60 9 = 69 Division made easy! Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain divisions. 42 ÷ 3 = ? 10 groups of 3 4 groups of 3 Chunks –12 –-30 - 30 - 12 0 0 12 12 4 chunks + 10 chunks = 14 42 Understand and use the principle of the associative law. Extend written methods to short division of HTU by U Choose appropriate number operations and calculation methods to solve word problems. What is associative law and do the majority of children care? Understand and use the principle of the associative law. Establish 5 x 16 is the same as 10 x 8 etc. 5 x 10 = 50 GRID! 5 x 6 = 30 = 80 Chunking! Extend written methods to short division of HTU by U 183 ÷ 5 = ? 183 – 150 (30 x 5) = 33 33 – 30 (6 x 5) = 3 Answer 36 r 3 To add/subtract by counting on or back in repeated steps of 1, 10, 100. Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain addition and subtraction. Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain multiplication. Use informal pencil and paper methods to support, record or explain divisions. Choose appropriate number operations and calculation methods to solve word problems.