* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Add this to your Formula Chart
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Numerical continuation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
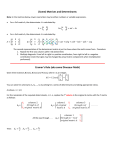
Cramer’s rule Determinants • Determinants are square arrays of numbers. • Each number in the array is an element • A two by two array is called a second order determinant. (2 rows and 2 columns) Second Order Determinants • This is the formula for solving a second order determinant. • To find the value of a second order determinant you take the difference in the cross products. Going from top left times bottom right subtracted by the bottom left times the top left as shown here------->. Example 1 • Find the value of the determinant. 3(5) – 4(2)= 3 4 2 5 =7 Cramer’s Rule • Another method for solving systems of equations • Cramer’s Rule utilizes determinants Add this to your Formula Chart Example 2 • Use Cramer’s Rule to solve the system of equations. 6x + 7y = -9 x - y =5 A = 6, B = 7, E = -9 C =1, D = -1, F = 5 Answer: ( 2, -3) X= -9 7 5 -9 5 -1 y= 1 5 6 7 6 7 1 -1 1 -1 Example 3 Two sides of a parallelogram are contained in the lines whose equations are 3x – 2y = -24 and 5x + y = -14. Find the coordinates of a vertex of the parallelogram. A =3, B = -2, E = -24, C = 5, D = 1, F = -14 Answer: ( -4, 6) -24 -2 3 -24 x= -14 1 y= 5 -14 3 -2 3 -2 5 1 5 1 Solve Systems on Calculator • www.analyzemath.com