* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.3 Determinants and Cramer`s Rule
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Singular-value decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Non-negative matrix factorization wikipedia , lookup
Orthogonal matrix wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Matrix multiplication wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Determinant wikipedia , lookup
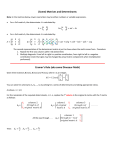
4.3 Determinants and Cramer’s Rule Determinants The the matrix D of a1 a 2 a1 b1 a2 b2 b1 b2 , symbolized has the value a1b2 a2b1. Note that the vertical bars are not absolute value signs, it is notation for determinant. Evaluate each determinant. 1. 8 2 3 7 2. 8 6 4 3 3. k 3k 2k 1 3 6k Given the system of equations with the coefficient matrix: a1 x b1 y c1 a1 a 2 a2 x b2 y c2 D a1 b1 a2 b2 The determinant of are the coefficient matrix Dx c1 b1 c2 b2 The x coefficients are replaced with the constants c1 and c2 b1 b2 Dy a1 c1 a2 c2 The y coefficients replaced with the constants c1 and c2 Cramer’s Rule for a System: Given the system of linear equations: a1 x b1 y c1 a2 x b2 y c2 If the D 0, then the system has exactly one solution. The solution is: Dy Dx y x D D *Note: If D = 0, the system has either no solution or infinitely many solutions. Use Cramer’s Rule to solve the system. 4. 2x y 1 5. 3x 2y 23 4x 6y 4 x 5y 14 D= Dx= Dy= D= Dx= Dy= Point of Intersection: Point of Intersection: Use Cramer’s Rule to solve the system. 6. 3x 4y 1 5x 7y 1 7. 7x 5y 0 5x 4 y 3 D= Dx= Dy= D= Dx= Dy= Point of Intersection: Point of Intersection: