* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity and Magnetism
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
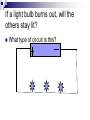
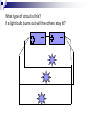
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide Vocabulary Charge Static electricity Electric field Measurement of an object’s extra positive or negative particles. Charge that stays on an object. Space around an object where electric forces occur. Vocabulary Electric current Circuit Electric cell conductor Flow of electric charges Path made for an electric current. Supplies energy to move charges through a circuit. Material that electric current can pass through easily. vocabulary Insulator Resistor Series circuit Parallel circuit Material that electric current can’t pass through. Material that resists but doesn’t stop the flow of current Circuit with one path for electric current. Circuit with more than one path for current. vocabulary Magnet Magnetic poles Magnetic field electromagnet Object that attracts things made of iron or steel. Ends of a magnet Space around a magnet where the force acts. Arrangement of wire wrapped around a core. An object has what charge if it has more negatives than positives? Negative When two objects both have positive charges, the objects……. Repel each other We use copper wire in our circuits because it ______________ electricity. Conducts A bar magnet’s pull is strongest at…. Both poles Magnets attract each other at… Opposite poles Name 3 ways to control and electromagnet. Turn the current on and off Add coils of wire around the core Decrease the amount of current by using a smaller battery If a light bulb burns out, will the others stay lit? What type of circuit is this? What type of circuit is this? If a light bulb burns out will the others stay lit? Essay questions What two magnets make a compass work? How do they interact? The earth is a large magnet. The needle of a compass is a magnet. The needle is attracted to the north and south poles of the earth. Essay question In what ways are electricity and magnetism alike? Both use a flow of electrons to push and pull objects. They both have positive and negatives. The opposites attract and repel. Essay question What will happen if you put a compass next to an electromagnet that is switched on? The compass needle will turn because an electromagnet produces a magnetic field. The compass needle will move to line up with the flow of electrons.