* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ELECTRICITY NOTES
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
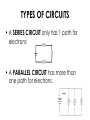
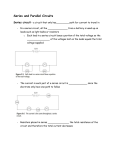
ELECTRICITY NOTES ELECTRICITY • ELECTRICITY: form of energy that occurs when electrons move from place to place • Electricity can form whenever (e-) electrons are gained or lost • All substances are made up of ATOMS which contain electrically charged particles called PROTONS and ELECTRONS • PROTONS have a positive (+) charge • ELECTRONS have a negative (-) charge • How can neutral substances become electrically charged? – When a neutral object slides past another object and picks up extra e– An object with more protons has a + charge – An object with more electrons has a charge STATIC ELECTRICITY • STATIC ELECTRICITY is a buildup of electrons on an object • CONDUCTORS: allow electrons to pass through easily – Examples: METALS, WATER • INSULATORS: do NOT allow electrons to pass through easily – Examples: NONMETALS When 2 objects are rubbed together they become CHARGED Objects with like charges REPEL Objects with opposite charges ATTRACT INDUCTION • INDUCTION occurs when a neutral object becomes charged by holding a charged object close to it (NOT touching) How is Earth’s Surface Charged by Induction? An ELECTROSCOPE is a devise that detects electric charge. A metal knob is connected to 2 metal leaves. When a charged object touches the knob, the leaves SEPARATE GROUNDING • GROUNDING: touching a charged object to the ground to remove extra charges Moving charges produce CURRENT ELECTRICITY which flows along a path called a CIRCUIT. Current that only flows in one direction is called DIRECT CURRENT (battery powered). Current that reverse its direction constantly is called ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC) (power company) ELECTRIC CURRENT (I) • THE FLOW OF e- (how many are flowing through each second) • Units: AMPERES (A) 1 AMPERE = 6.25 X1018 e- EACH SECOND ELECTRIC CELL • An ELECTRIC CELL is a devise that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. 2 or more electric cells combined make up a BATTERY. • An electric cell contains two different substances called ELECTRODES. The electrodes are places in a conducting mixture called an ELECTROLYTE. Chemical reactions take place between the ELECTRODES and the ELECTROLYTE. • Wet Cell: a battery with a liquid electrolyte…acid (car battery) • Dry Cell: battery whose electrolyte is a paste instead of a liquid (AA, C, D batteries, etc) • Anode: - end of battery where e- leave the battery • Cathode: + end of battery where ereturn to the battery • VOLTAGE (V) also called POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE. It is the difference between one end of the power source and the other end. – Units: VOLTS (V) RESISTANCE (R) • RESISTANCE is the opposition to electron flow. Conductors have LOW resistance. Insulators have HIGH resistance. – Units: Ohms Ω • Resistance depends on TEMPERATURE, DIAMETER, LENGTH, METVAL vs. NONMETAL Ohms Law V = IR voltage = current x resistance The filament in a light bulb uses a current of 0.5 A when the voltage is 120V. What is its resistance? Circuits • A path for electrons to travel through is called an ELECTRIC CIRCUIT • If an electron can flow in a complete path, the circuit is A CLOSED CIRCUIT • If a connection is broken along the circuit, it becomes AN OPEN CIRCUIT • Switch: A DEVICE THAT CAN OPEN A CIRCUIT Simple Circuits • Made up of 1. power source (battery, generator) 2. conductor (wire) 3. load (bulb, resistor, motor) SAFETY DEVICES on CIRCUITS that PREVENT FIRES 1. CIRCUIT BREAKER: switch that opens when current is too high 2. FUSES: a switch that melts when current is to high TYPES OF CIRCUITS • A SERIES CIRCUIT only has 1 path for electrons • A PARALLEL CIRCUIT has more than one path for electrons. Short Circuits • Short Circuit: when uninsulated wires touch and the e- take a shorter path; can overheat and cause a fire Electric Power The amount of electrical energy used each second is called ELECTRIC POWER , RATE AT WHICH ENERGY IS CONVERTED Units: Watts (w) or Kilowatts (kW) Formula: P = VI Power = Volts x Current How much electrical power is used by a TV that uses a current of 0.5A when connected to a voltage of 120V? Electrical Energy Power E = Pt energy = power x time A hairdryer with a power rating of 1500W is used for 120 seconds. How much electrical energy does it use? Kilowatt-hour • The unit for energy used by the power company






































![Electricity Review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004366833_1-3acacfb89ebe2cacb343dbc81ffd5d6c-150x150.png)
