* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity - science
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
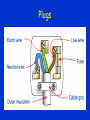
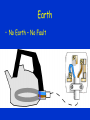
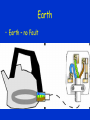
Electricity Current Voltage Resistance Current, Voltage, Resistance characteristics AC DC Plugs Earth Fuses Power Current • Current is the amount of charge flowing past a point in a given time Current (A) = Charge (C) / time (s) Current read by an ammeter – connected in series Potential Difference • Voltage • Potential difference is the energy given to or given by a charge when it passes a component. PD (V) = Energy (J) / Charge (C) PD is taken by a voltmeter and is connected in parallel with the component. Resistance • Resistance is the volts per amp for a component. • How many volts are needed to push a current of so many through a component. Resistance (Ohms) = PD (V)/ Current (A) • Circuit models • Circuit diagrams • Resistor models IV Characteristics • Resistor • Bulb • Diode Resistors • Thermistor • LDR • review Mains Elec • PHET • AC DC • Period and frequency Plugs Fuse • A Fuse is a piece of wire with a low melting point • If there is a fault in the electrical appliance and the current goes up it could damage the wiring in the appliance • But if a fuse is installed, this will melt (or “blow”) and break the circuit • So a fuse is used to protect the appliance – not necessarily to protect us from electric shock Earth • What on Earth does it do? • VdG Earth • No Earth – No Fault Earth • No Earth - Fault Earth • Earth – no Fault Earth • Earth - Fault Power • Power = work done / time taken • Lifting stuff Electrical Power • Electrical power is the electrical work done in a given time. Power (W) = current (A) x voltage (V)