* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phrases and Clauses
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
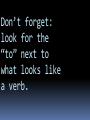
TYPES OF PHRASES A phrase is: A group of related words that is used as a single part of speech. It does not have both a subject and a verb, so it is never a complete sentence. Three types of phrases Prepositional phrases Appositive phrases Verbals and verb phrases Prepositional Phrases Contain a preposition (those small words of location—in, on, under, over, beside, etc.) Have a preposition and a noun (the object), and sometimes a word in between. On the road Over the river To the gym Beside the ducks from Grandma in my backpack How to remember prepositional phrases: Think about anywhere a cat can go. Over the chair Under my car tire Around the circle Of my friend (Oops! Not foolproof) Through the yard Some prepositions that don’t necessarily show location: About By To With Of Prepositional phrases Can be adjective Can be adverb modifies noun or Modifies verb, adjective, pronoun Tells what kind or which one or adverb Tells how, when, where, why, or to what extent Adjective prepositional phrases The members of the club want sweatshirts with the club emblem. Here’s a letter for you from Grandma. The light in the kitchen is on. Adverb prepositional phrases The man answered with a smile. Chris will be finished by Wednesday. They sailed across the lake today. The calculations were wrong by three inches. My sister works part-time for extra money. Adjective or Adverb Phrase? The plane taxied down the runway. Getting a candy reward was one reason for the students’ hard work. He was the most successful president of the club. We flew across the International Date Line. Second kind of phrase: APPOSITIVE Gives information which helps us be POSITIVE that we know what is being discussed. Appositive Phrases In each of the examples, the underlined part is the appositive. “Larry, the plumber, fixed the sink. An excellent dancer, Rebecca took years of lessons. Miss Piggy, Kermit’s girlfriend, won first prize, a pot-bellied pig. NEXT PHRASE TYPE:Verb When a word that looks like a verb really functions as a different part of speech in a sentence, it is called a VERBAL. Huh? A verb that isn’t really a verb is a verbal?? Sam, the duck! This is stupid. I don’t get it. Important Concept: The part of speech depends on how a word is used in a real sentence. There are three types of verb phrases: 1. Infinitive 2. Participial 3. Gerund Grammar is stupid. Grammar is stupid. Grammar is stupid. One type of Verb phrase: Infinitive Clue: look for the word “to” next to what looks like a verb. Example: “Sam likes to eat.” Don’t forget: look for the “to” next to what looks like a verb. Another type of verbal: participle A participle is a word ending in -ing or -ed that helps describe something. Participles function as adjectives because they describe or explain. Sometimes participles end in other ways if they are formed from irregular verbs (like frozen) Three examples of participles. We watched an exhausting Powerpoint. The receiver made a diving catch. The man admired the painted barn. Participial phrases Participles can also be in phrases. Look for “ing” or “ed”. The people standing in line grew irritated. Which people? The ones standing in line. Determined to make the team, Jo shot baskets every night. For what reason did Jo shoot? Because she’s determined to make the team. Third type of phrase: Gerund A gerund ends in –ing A gerund always functions as a noun. Gerunds: end in -ing You can learn a lot from studying. You can learn a lot from what? Studying. You could hear laughing all the way down the hall. What could you hear? Laughing. If you can ask a “what” question, and the word answers it, then it is a noun—a gerund. Gerunds in phrases A gerund can also be in a phrase: Laura enjoyed vacationing in Michigan. Laura enjoyed what? Vacationing in Michigan. REVIEW: A phrase is a group of words that functions as a single part of speech. A phrase doesn’t have both a subject and a verb, so it is never a complete sentence. The three types of phrases are: Prepositional Appositive Verbals and verb phrases Participial (Adjective) Gerund (noun) Infinitive (has the word “to” + verb)