* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gerunds and Infinitives - UNAM-AW
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Spanish verbs wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Finnish verb conjugation wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
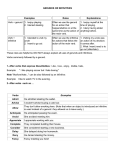
Gerunds A gerund is a verb-ing that is used as a noun. Gerunds are used: As the subject of a sentence. With a verb: verb + gerund (object of the sentence) With a preposition: preposition + gerund (a gerund is the only kind of verb that can follow a preposition) With a possessive: possessive + gerund Gerund as the subject of the sentence: Hiking is a good activity to do in the summer time. Can have a negative form: Not drinking water on a hot day is dangerous, Gerunds are always singular even when they are used as part of a phrase. Use a singular verb with them. Eating too many calories is unhealthy. Gerunds can follow certain verbs (see chart) and they become the object of the verb. I like riding my bike because it keeps me healthy. Gerunds are also used with possessives. I dislike George’s eating fast food. (In spoken English people usually use nouns or object pronouns instead of the possessive) Gerunds can follow a preposition and they are the only verb form the can do this. She read an article about fighting in hockey. Infinitives An infinitive is used after some verbs and is used as a noun. The form is to + verb. Infinitive + verb (subject) Verb + infinitive (object) Verb + object/object pronoun + infinitive Adjective + infinitive As the subject of a sentence: To procrastinate causes a lot of problems. As the object of a sentence: I always like to watch movies on the weekend. After an object: She wanted him to fix her car. After an adjective: George was afraid to fail. (The adjective describes the subject and tells the subjects feelings about an action.) When forming the negative, use not + infinitive They are careful not to give their children a lot of candy. Gerund OR Infinitive Some verbs can be followed by either a gerund or infinitive. In most cases there is no difference in meaning. She started singing. She started to sing. If the main verb is in the progressive form, use an infinitive only. It is beginning to rain. NOT: It is beginning raining. The verbs “remember” “forget” “regret” “try” and “stop” can be followed by a gerund or infinitives BUT the meaning changes. I stopped eating pizza because I’m on a diet. (I will not eat pizza anymore) I stopped to eat pizza because I was hungry. (I stopped doing what I was doing in order to eat pizza.) She remembered to turn off the light when she left. (she turned off the lights) She remembered playing with dolls when she was young. (she recalled the memory of playing with dolls)