* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PARTS OF SPEECH REVIEW
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
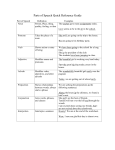
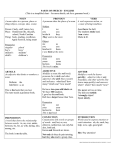
A word used to name a person, place, thing or idea. › Ex. Friend, manager, belief, love A PROPER NOUN names a particular person, place, or thing. › The Cage, Paris, Mother Teresa A word used in place of one or more nouns. › Some examples: I, you, he, she, it, they, me, him, her, us, them, myself, yourself, my, mine, your, yours, etc. *Review your sheets from earlier for a longer list A word used to modify (or describe) a noun or a pronoun. › An adjective answers one of three questions about the word it modifies. Which one? That kitten, this classroom, the tall one What kind? Blue pen, wonderful book, large truck How many? Five cents, many papers, several windows A word that expresses action or helps make a statement Action verb: expresses either physical or mental action. The verb think, which expresses mental action, is an action verb just like kick, which expresses a physical action. › Example: Mother works for the school. Linking verb: links a noun with a noun or a noun with an adjective. › Examples: › Am, is, are, was, were, seem, appear, etc. Look at notes for a larger list of examples. NOTE: if you can put is, are, was, or were in place of the verb without changing the meaning of the sentence, it is likely a linking verb. The helping verb: often a verb can consist of more than one word. Thus, verbs that precede the main verb are called helping verbs. › Some common examples: › Be (am, is, are, was, were, been), shall, will, have (has, had), etc. Ex. I should study. Should is the helping verb and should study is the full verb phrase. Look at notes for further list. Word used to modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. It usually tells something about the verb. › How – Look closely. (Closely modifies look) › When – We lost recently. (Recently modifies lost) › Where – Hang the poster here. (Here modifies hang) › How Often – Norma usually drives to school. (Usually modifies drives) Adverbs typically end in –ly. › Ex. Always, finally, slowly, etc. Some adverbs modify adjectives. › We read a really good book. (Really modifies the adjective good) Some adverbs modify other adverbs. › She walks too slow. (Too modifies the adverb slow) Word used to show the relationship of a noun or a pronoun to another word in the sentence. A group of words beginning with a preposition and ending with a noun or pronoun is called a prepositional phrase. Examples: › Under the bed › Through the door › After the sign NOTE: Study ALL prepositions found from previous notes so you can easily recognize them for the midterm. Word that connects words or group of words (and, but, and or). › Examples: Tonya is happy and excited. Is it snowing or raining? I can dance, but I cannot sing. An exclamation that expresses emotion. It has no grammatical relation to the rest of the sentence. › Examples: Whoa! Watch where you are going! Wow! That looks amazing! Oh, it’s not important. A clause that can stand by itself, expressing a complete thought. It always has a subject and a verb. › Examples: The man wore a black coat. I cannot go to the store. A clause that cannot stand on its own because it does not express a complete thought. A dependent clause is different from a prepositional phrase because it contains both a subject and verb whereas a prepositional phrase does not. › Examples: Although she is sick, the young woman still goes to work. (dependent clause) Under the tree, you will find a basket of goodies. (prepositional phrase)