* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CS465 Slides - Regis University: Academic Web Server for Faculty
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Comparison of command shells wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
History of Unix wikipedia , lookup
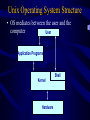
CS465 Introduction to UNIX What is UNIX? (1) • UNIX is an Operating System (OS). • An operating system is a control program that allocates the computer's resources, schedules tasks, and helps the user communicate with the computer. • Most popular PC operating systems: Windows 95/98/2000/XP -- proprietary, single-user OS • UNIX was developed long before Windows, about 30 years ago at AT&T Bell Labs (95% written in “C” programming language). What is UNIX? (2) • UNIX was designed as an operating system for experts, used on high-end workstations, servers and hosts. • UNIX provides some powerful features: – Interactive, multi-user support – Security - private and shared files – Inter-process communication – Extensive network support History of Unix • 1970-1974 – Early stages, developed on PDP-11 machines – Unix is not an acronym, but a weak pun on MULTICS • • • • • • • • 1976, first licensed release, Version 6 1978, first portable version, Version 7 1979, Berkeley 3 BSD 1983, System V as industry standard 1984, Microsoft releases Xenix 1986, BSD 4.3, AT&T Version 9 1987, SVR4, Mach, … 1993, Linux UNIX Compared with other OS • • • • • • Mature and stable OS Large user community Vendor-independent OS Network-portable window system (X) Runs on range of hardware (PC - Cray) Common Open System Environment (COSE) – Source code is available to view and modify Multi-user, Multi-tasking • More than one user can run at the same time and each user can run more than one task at the same time • In Unix, each program is started as a process. – A process is a program in execution. • Usually only one copy of a program, but there may be many processes running the same program. • Each interactive user may have: – only one process in foreground – may have several processes in background Most Important Feature of UNIX • Most important feature of UNIX: STABILITY – 30 years to get the bugs out – Important in shared environments and critical applications • Shared Environments Example: University – Windows NT crashes at least once a day in labs – UNIX servers crash about once a semester (usually due to hard disk failure) – UNIX more than 100 times more reliable than Windows! UNIX Versions • Two main types of UNIX: – BSD (Berkeley Software Distribution)/OSF – System V (developed at AT&T) our book • Different versions of UNIX for different hardware: – Sun Microsystem’s Solaris (and SunOS) – Hewlett-Packard’s HP-UX – IBM’s AIX – SGI’s IRIX Cornerstones of the Unix Philosophy 1. Clean minimal design (nothing unnecessary) • Make each program do one thing well. 2. Combine existing utility programs to perform more complex tasks, and allow users to build their own utility programs. 3. Use terse commands and messages to reduce typing and screen output. 4. Allow users to select what command language they will use (shell selection). Additional Unix Philosophy 6. Make file, device, and interprocess I/O compatible. - All three are treated like files 7. Open access: - Minimal restrictions to the ways of doing things - User can be very creative (and frustrated). 8. Major parts of the Unix OS: - Kernel - Shell - File System Unix Operating System Structure • OS mediates between the user and the computer User Application Programs Kernel Hardware Shell The Unix Kernel • Loaded at system startup (boot up) and is memory-resident – Directly controls the hardware • Manages all devices – Schedules work done by the CPU – Manages memory and allocates it to each process • Gets instructions from shell and carries them out • Enforces access permission on the file system The Shell • Command interpreter – To get your work done, you enter commands at the shell prompt – Can edit the command line – Shell interprets the command and passes it to the kernel for execution • Allows you to create a customized environment • Stores and allows manipulation of command history • Used to write shell scripts Shells (1) • Bourne Shell: the default shell (sh) – original Unix shell, written by Steve Bourne – does not have interactive features of newer shells – widely used for writing shell scripts – available on ALL Unix systems • C Shell (csh): originally written for BSD – with syntax similar to the C language – with many enhancement over the Bourne shell. Shells (2) • Korn Shell (ksh): AT&T’s answer to C Shell – Superset of the Bourne shell – Also includes many C shell features – very efficient, written by Dave Korn • TC Shell (tcsh) – Superset of C shell with EMACS-like command line editing • Bourne Again Shell (bash) – Public domain shell written by the Free Software Foundation Why has Unix been successful? • UNIX is portable, because it was written in C. – Provides hardware independence. • Open System – Underlying operating system source code is available • Provides a productive environment – Allows multi-tasking and sharing of data – Excellent C development environment is built-in – Networking capabilities are built in Unix Disadvantages UNIX is not as user-friendly as some operating systems – Command names are often cryptic – User help is not great UNIX does not error check user commands to protect users from hurting themselves or the system – Example: Request to copy a file over an existing file will overwrite the existing file with no warning. Unix Disadvantages UNIX is less secure than some operating systems – Developed to be used as a software development environment, in which all users are working together cooperatively. Security was traded for more convenience and flexibility. – Well-documented open code makes hacking easier. UNIX's portability also makes it less efficient on any particular hardware. – Proprietary operating systems are optimized for that hardware. I hope that you will decide that Unix’s advantages outweigh its disadvantages!