* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Spread of Christianity
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Aachen Cathedral wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Patrimonium Sancti Petri wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
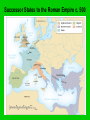
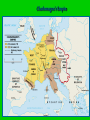
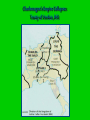
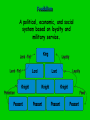
Foundation of Feudal Europe • Hard-won political order: based on highlydecentralized but flexible system that vested political, military, & judicial authority in local & regional rulers • Long, slow process of economic recovery – manorial system followed by increased trade, industry, commerce, & reurbanization • Cultural unity – the Church – papacy & monastic movement The Quest for Political Order The Germanic Successor States, c. 500 CE • Last Roman emperor deposed by Germanic Odoacer, 476 CE • Administrative apparatus still in place, but cities lose population • Germanic successor states: – Spain: Visigoths – Italy: Ostrogoths – Gaul: Burgundians, Franks – Britian: Angles, Saxons Successor States to the Roman Empire c. 500 The Frankish Empire • In the territory known as Gaul, and what is currently the country of France, the Franks emerged as the dominant tribe in the area. • In the late 400’s, Clovis was the first king of the Franks to unite all the Frankish tribes under one ruler. His conversion to Christianity gained him a great ally in the Roman Catholic Church. The Franks • Heavy influence on European development • Strong agricultural base • Shifts center of economic gravity to Europe • Firm alliance with western Christian church Essential Question What is the significance of Clovis’s conversion to Christianity? Clovis (ruled 481-511) • Major Frankish leader • Destroyed last vestiges of Roman rule in Gaul • Dominated other Germanic peoples • Franks establish themselves as preeminent Germanic people Clovis’ Conversion to Christianity • Paganism, Arian Christianity popular among Franks • Clovis and army chooses Roman Catholicism • Influence of wife Clotilda • Political implications: – Alliance with western church The Carolingians • Charles “The Hammer” Martel begins Carolingian dynasty • Defeats Spanish Muslims at Battle of Tours (732) – Halts Islamic advance into western Europe Charles de Steuben's Bataille de Poitiers en Octobre 732 depicts a triumphant Charles Martel (mounted) facing ‘Abdul Rahman Al Ghafiqi (right) at the Battle of Tours. The Carolingian Empire Essential Questions What were the contributions of Charlemagne’s reign? Why did it ultimately fail to last very long? Charlemagne (r. 768-814) • Grandson of Charles Martel • Centralized imperial rule • Functional illiterate, but sponsored extensive scholarship • Major military achievements Charlemagne’s Empire Charlemagne’s Administration • • • • Capital at Aachen, Germany Yet constant travel throughout empire Spread Christianity Set Up Education System – Increased Scriptoriums – Alcuin, the leading scholar and educator under Charlemagne introduced the 7 liberal arts • Begins Romanesque Architecture • Expansion of Territory • Imperial officials: missi dominici (“envoys of the lord ruler) – Continued yearly circuit travel Romanesque church in Normandy Romanesque church in Poland Charlemagne as Emperor • Hesitated to challenge Byzantines by taking title “emperor” – Yet ruled in fact • Pope Leo III crowns him as emperor in 800 – Planned in advance? – Challenge to Byzantium Pope Crowned Charlemagne Holy Roman Emperor: Dec. 25, 800 The Carolingian Renaissance Carolingian Miniscule Louis the Pious (r. 814-840) • Son of Charlemagne • Lost control of courts, local authorities • Civil war erupts between three sons • Empire divided in 843 Charlemagne crowns Louis the Pious Charlemagne’s Empire Collapses: Treaty of Verdun, 843 Invasions • South: Muslims • East: Magyars • North: Vikings – Norse expansion begins c. 800 CE – Driven by population pressure, hostility to spread of Christianity – Superior seafaring technology – Sailed to eastern Canada, northeastern US The dissolution of the Carolingian Empire (843 CE – divided amongst Charlemagne’s grandchildren) and the invasions of early medieval Europe in the ninth and tenth centuries Essential Questions Who were the Vikings? What were the motivations behind their behavior? What were their accomplishments? How did they disrupt European society? The Vikings • From village of Vik, Norway (hence “Viking”) • Boats with shallow drafts, capable of river travel as well as open seas • Attacked villages, cities from 9th century – Constantinople sacked three times • Carolingians had no navy, dependent on local defenses England • Viking invasions force consolidation of Angles, Saxons and other Germanic peoples under King Alfred (r. 871-899) • Built navy • Fortified cities against attack Germany and France • King Otto of Saxony (r. 936-973) defeats Magyars, 955 • Proclaimed emperor by Pope in 962 • Establishment of Holy Roman Empire • France endures heavy Viking settlement • Loss of local autonomy Essential Questions? What were the obligations of lords toward their retainers and the retainers toward their lords? Why was this arrangement often unstable? Early Medieval Society • Concept of Feudalism – Lords and vassals – Increasingly inadequate model for describing complex society • Ad hoc arrangements in absence of strong central authorities Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service. Organizing in a Decentralized Society • Local nobles take over administration from weak central government • Nominal allegiances, esp. to Carolingian kings • But increasing independence Lords and Retainers • Formation of small private armies • Incentives: land grants, income from mills, cash payments • Formation of hereditary class of military retainers • Development of other functions – Justice, social welfare Potential for Instability • Complex interrelationship of lord-retainer relations • Rebellion always a possibility • Nevertheless, viable large states developed (Germany, France, England) Essential Question What role did the serfs play in early medieval Europe? What was life like on the manor? Origins of Serfdom • Slaves, free peasants in both Roman and Germanic societies • Heavy intermarriage • Appeals to lords, special relationships • Mid-7th century: recognition of serf class – Midway between slave and free peasant Serfs’ Rights and Obligations • Right to pass on land to heirs • Obligation to provide labor, payments in kind to lord • Unable to move from land • Fees charged for marrying serfs of another lord Manors • Large, diverse estates • Lord provides governance, police, justice services • Serfs provide labor, income The Medieval Manor Life on the Medieval Manor Serfs at work Women in the Middle Ages • Noblewomen were responsible for the entire running of an estate while her husband was in battle. • All women had very limited inheritance rights, as all possessions went to the oldest son. • In the Middle Ages, the Church portrayed women as weak and easily tempted into sin. Yet, women were also portrayed as modest and pure in spirit. • Learning was generally discouraged for women. Essential Questions What was the significance of the invention of the heavy plow for the European economy? Although trade constricted in the early middle ages, where and how was it still going on? The Economy of Early Medieval Europe • Agricultural center moves north from Mediterranean • 8th century iron-tipped plow introduced in Europe • Draft animals bred • Water mill technology • Agricultural output insufficient to support growth of cities • Strong Mediterranean trade despite Muslim domination of sea Norse Merchant Mariners • Commerce or plunder as convenient • Link with the Islamic world for trade Population Growth of Europe, 200-1000 CE 40 35 30 25 20 Millions 15 10 5 0 200 400 600 800 900 1000 The Formation of Christian Europe • Clovis’ conversion forms strong alliance with Roman Christianity • Church supplies Clovis with class of literate information workers: – Scribes – secretaries The Franks and the Church • Protectors of the Papacy • Charlemagne destroys Lombards, who threatened Pope, Rome • Spreads Christianity in northern areas • Support of scholarship, scribal activity The Spread of Christianity • Charlemagne fights pagan Saxons (772804) – Saxons later adopt Christianity • Scandinavia, other pockets of paganism until c. 1000 CE Essential Questions What was the role of the pope in the early middle ages? How did his role evolve over this period of time? Pope Gregory I (590-604 CE) • “Gregory the Great” • Asserted papal primacy • Prominent theologian – Sacrament of penance • Major missionary activity, especially in England Essential Questions How did monasticism develop in early medieval Europe? What was the significance of the monasteries to the European society and economy? Monasticism • Egyptian origins, 2nd-3rd centuries • Monastic lifestyle expands 4th century • Large variety of monastic rules – Range from extremely ascetic to very lax St. Benedict (480-547) • Established consistent rule for monasteries – Poverty – Chastity – Obedience • St. Scholastica (482-543) – Sister of St. Benedict – Adapts Benedictine Rule for convents A late 15th-century Scriptorium by of Jean Miélot In the strictest definition of illuminated manuscript, only manuscripts with gold Pope Gregory I, by or silver would be Francisco de Zurbarán considered illuminated. St. Benedict by Fra Angelico, c. 1437-1446 Monasticism and Society • Accumulation of large landholdings, serfs • Social welfare projects – Esp. labor contributions • Expansion of literacy • Inns, orphanages, hospitals The Power of the Medieval Church The church controlled about 1/3 of the land in Western Europe. Tithe 1/10 tax on your assets given to the church. Threat of excommunication and an inderdict gave the church tremendous control over European peasants and nobles. The selling of indulgences, canon law and simony also fortified the church’s power, but led many to recognize these acts as corrupt. Church Secular Influence & Pope Innocent III • The Church claimed authority over all secular rulers, many of whom did not recognize this authority, often resulting in power struggles between monarchs and popes. • When King John of England challenged Pope Innocent III over the appointment of an archbishop, he was excommunicated in 1209. Magna Carta, 1215 King John I “Great Charter” Monarchs were not above the law. Kings had to consult a council of advisors. Kings could not tax arbitrarily. The Medieval Church • Everyday Life – Christians attend village churches – Priests run village churches – All Christians pay tithe • Power of the Church – Pope leads – Canon Law – Excommunication/ interdict • Reform -Church wealth & influence - Some clergy corrupted - Reformers • Nuns & Monks -Set up housing, hospitals, schools - Missionaries Preservation of learning