* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Loop and Nodal Analysis and Op Amps
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
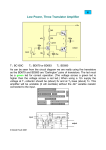
Electronic Circuits Laboratory EE462G Lab Background, Procedures, and Overview History of Electronics Vacuum Tubes Developed by Lee DeForest (1906) Used in amplifiers and switching devices Led to spread of radio broadcasting 1920’s, Television 1930’s, electronic computers 1940’s Educational Links http://www.paia.com/~paia/tubworks.htm History of Electronics Solid-State Transistors Developed by William Shockley, John Bardeen, Walter Brattian (Bell Labs) (1947) Similar applications as vacuum tube except it requires less power, has a lower manufacturing cost, performs more robustly, and could be miniaturized. Educational Links http://www.williamson-labs.com/480_xtor.htm http://www.milbert.com/tstxt.htm http://www.pbs.org/transistor/ N-Type Silicon N-Type Silicon P-Type Silicon History of Electronics Integrated Circuits (ICs) Developed by Jack Kilby (TI), and by Noyce and Moore (Fairchild Semiconductor) (1958). Multiple transistors, resistors, and capacitors, fabricated on a single wafer (chip) and could be made very small. Educational Links http://www.uoguelph.ca/~antoon/circ/circuits.htm http://members.tripod.com/michaelgellis/tutorial.html http://bftgu.solarbotics.net/starting_elect_ic.html http://invention.smithsonian.org/centerpieces/quartz/technology/integrated.html Electronic Components Studied Diodes pn junction Zener Transistors Effect Transistors – (FETs) Bipolar Junction Transistors – (BJTs) Field The first transistor http://www.mtmi.vu.lt/pfk/funkc_dariniai/transistor/ http://www.interq.or.jp/japan/se-inoue/e_diode.htm Nonlinear Device Characterization To measure nonlinear device characteristics, voltage/current amplitudes are swept over input terminals while measuring current/voltage across output terminals (analogous to sweeping frequencies in linear RLC circuits while measuring amplitude and phase changes between input and output – What is this characterization called?). Curve tracers systematically sweep voltage amplitudes over two terminals of a device while measuring the resulting current. The current-voltage relationships is referred to as the transfer characteristic (TC) curve of the device. Why is the TC NOT a good model for linear devices? What would the TC curve or an ideal resistor look like? Instrumentation - Oscilloscope http://www.tek.com/site/ps/0,,41-12482-INTRO_EN,00.html Tektronix’s Oscilloscopes TDS3012B Key operating concepts •Vertical scale adjustments •Horizontal scale adjustments •Trigger adjustments •Earth ground connections Instrumentation - Multimeter http://www.tek.com/Measurement/cgi-bin/framed.pl?Document=/Measurement/Products/catalog/cdm250/&FrameSet=other Tektronix’s Multimeter CDM250 Key operating concepts •Connections for voltage, current, and resistance measurements •Selection of scale for measurement •Ground connections Instrumentation – Power Supplies http://www.tek.com/site/ps/0,,40-10199-INTRO_EN,00.html Tektronix’s PS280 DC Power Supply: Key operating concepts: •Setting and limiting DC voltages and currents •Connecting chassis and earth grounds Instrumentation – Function Generator http://www.tek.com/site/ps/0,,76-12019-INTRO_EN,00.html Tektronix’s Function Generator AFG310 Key operating Concepts •Selecting waveforms •Selecting waveform parameters •Grounding issues Instrumentation – Curve Tracer http://www.tek.com/site/ps/0,,76-10757-INTRO_EN,00.html Tektronix’s Curve Tracer 370B Key Operating Concepts •Voltage sweep pattern selection •Horizontal and vertical scale adjustment •Step changes for third terminal voltage or current •Device socket plug Laboratory Component Supplies Parts can be purchased from the IEEE parts store (http://ieee.uky.edu/) located in Room 560 PFAT Individual components: Breadboard - 1 Wire kit bag - 1 Laboratory Component Supplies Resistors: 10 ohm (3) 100 (3) 510 (3) 1K (3) 2.2K (3) 5.1K (3) 10K (3) 22K (3) 100K (3) 180K (3) 220K (3) 470 (1) 1K (1) 1.2K (1) 1.6K (1) 2K (1) 3.3K (1) 11K (1) 1Meg (1) Laboratory Component Supplies Capacitors: 0.022µF (3) 2.2µF (3) 10µF (3) 47µF (3) 100µF (3) Diodes: Diode- IN4001 (4) Zener diode- IN964A (1) BJT: NPN, PN2222 (2) MOSFETs: n-channel MOSFET- ZVN3306-ND (4) p-channel MOSFET- ZVP3306-ND (2) Course Web Links Syllabus http://www.engr.uky.edu/~donohue/ee462g/sylee462g.html Supplies http://www.engr.uky.edu/~donohue/ee462g/ee462supplies.pdf Lab Assignments http://www.engr.uky.edu/~donohue/ee462g/labee462g.html Lecture Notes http://www.engr.uky.edu/~donohue/ee462g/lecee462g.html Special Assignment 1 Download and read through tutorial on oscilloscopes (~50 Pages), “The XYZs of Oscilloscopes” http://www.tek.com/Measurement/App_Notes/XYZs/03W_8605_2.pdf 1. 2. 3. 4. Print out pages 51 through 55. Put your name on the first page and complete the written exercises. Use the answer key to determine number of wrong responses, put that number on the front page next to your name and circle it. On a separate sheet of paper, briefly describe (10 to 15 sentences) how an analog oscilloscope displays a periodic waveform. Assume the trigger is set to the same channel as the periodic waveform being displayed. Be sure to clearly describe the relationship between the trigger, oscillating signal, and CRT sweep rate. The reader should have a good idea why a periodic waveform appears stationary on the oscilloscope. You can sketch diagrams if that helps your explanation. Attach all pages together and hand in at the beginning of the next lecture period. The assignment grade will depend on completing 1 through 3 and the quality of the explanation in 4.