* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Historical Background and Context for Middle East History
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic monuments in Kosovo wikipedia , lookup
History of the Muslim Brotherhood in Egypt (1928–38) wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic extremism in the 20th-century Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Protestantism and Islam wikipedia , lookup
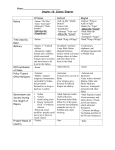
Historical Background and Context for Middle East History • • • • Rise of Islam Early history – political implications Spread of Islam The Ottoman Empire circa 18-19th centuries The Rise of Islam • Arabian context • Muhammad the prophet • The message The Rise of Islam • • • • Political implications Islam the religion The Quran The appeal of Islam Periodization in the History of the Islamic Middle East • Antiquity: from the rise of civilization to the coming of Islam • Classical Islamic period: from the life of the prophet Muhammad to the middle of the 10th century A.D. • The early medieval era: from about 950 to about 1250 • The late medieval era: from about 1250 to about 1500 • The early modern era: from about 1500 to about 1800 • The modern Middle East: from about 1800 to the present The Expansion of Islam, 632-733 A.D. The Spread of Islam • Umayyads – Damascus, 661-749 • Abbasids – Baghdad, 7501258 • Islamic state and society • 1258-1700s – Mongol invasions; fragmentation; Mamlukes • 1300s – rise of the Ottoman Turks Baghdad Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire • Key dates: – 1453 (Mehmet II) – 1514 (Selim I) – 1529 (Suleyman) • Source of power – Military – Ruling strategy – Local autonomy • Distinguishing characteristics – Polyethnic and Tolerant – Flexible Suleymaniye complex, Istanbul Ottoman Empire, cont. • 4 principles of rule: – 1) expansionary – 2) notions of dynasty, rights, responsibilities of rulers as Islamic figures – 3) tolerance of local practices and customs – 4) division of society into ruler/ruled Ottomans: State and Society • Land and revenue • Islamic law • Sunni legitimacy • Military • Government • Ottoman culture Suleyman the Magnificent "I, the Sultan of Sultans, the leader of the lords, the Khan of the sovereigns of the world, the shadow of God on earth, the Sultan and Padisah of the Mediterranean and Black sea, Romania, Anadolu, Karaman, Diyarbakir, Iran, Azerbaijan, Syria, Egypt, Mecca, Medina, and all Arab lands. I am Sultan Suleyman, the son of Selim Han, and you Francis, King of the province of France. You have send a letter to my court informing me that the enemy has entered your country and imprisoned you. Asking for grace and support, hoping for your freedom. Now, it is not befitting for rulers to cower, and to be imprisoned. Keep your spirits high, you will learn our decision from your men. (Letter from Suleyman the Magnificent to Francis I, King of France, 1536)