* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Trapezoids
Group (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
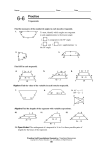
Trapezoids Jude Saint-Jean Dapo Brandon Period:12 Definition A quadrilateral which has at least 1 pair of parallel sides A trapezoid with 1 pair of congruent sides Properties of sides The bases (top and bottom) of an isosceles trapezoid are parallel. Opposite sides of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent. The angles on either side of the bases are congruent. The bases (top and bottom) of a trapezoid are parallel. That's it. No sides needs to be congruent and no angles need to be congruent. Properties of angles Adjacent angles along the sides are supplementary. Base angles of isosceles trapezoid are congruent. Normal trapezoids don’t have any special properties. Proof Given: <a=102 & <d is adjacent to <a & it’s an isosceles trapezoid <a = 102 Prove: <d is supp. to <a Given Same side interior angles <a is congruent to <b Angle property of quadrilateral(1,2) <a+<b+<c+<d = 360 Same side interior angles(3) <c is congruent to <d Addition property(4) <d is supp. to <a Properties of diagonals The diagonals (not show here) are congruent. Nothing special happens with the diagonals. Lines of symmetry A regular trapezoid has no lines of symmetry Isosceles trapezoids have only 1 line of symmetry formulas Perimeter = a + b + c + B Area = 1/2h(B+b) Area of parallelogram (B+b) x h But, this is double of what we need... So, multiply by 1/2. Other facts Altitude: The altitude of a trapezoid is the perpendicular distance from one base to the other. (One base may need to be extended). Median: The median of a trapezoid is a line joining the midpoints of the two legs. Connection to coordinate geometry Trapezoid and its properties. (Coordinate Geometry) Trapezoid area and perimeter. (Coordinate Geometry) Websites Mathopenref.com Coolmath.com