* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth and Atmoshere Revision
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
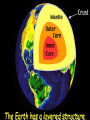
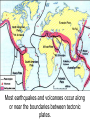
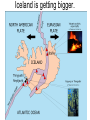
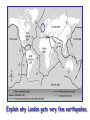
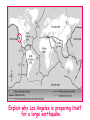
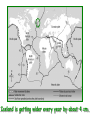
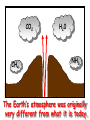
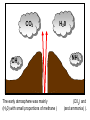
‘Winners never quit and quitters never win.’ What does this mean? B1 Revision 1. Chromosomes are found in? A B C Just in brain cells The nucleus of a cell Cytoplasm 2. Cloning refers to .. A Techniques that are used to produce genetically identical individuals ? B Techniques that are used to produce genetically different individuals 3. Which statement is incorrect about Sexual reproduction… A B There is only one parent. The offspring is a clone Results in variation in the offspring of parents C The new cell gets half its genes from 2 parents D Involves a sex cell fusing with a female sex cell 4. Gametes are … A C Male and Female sex cells (sperm and egg) Male sex cells (sperm) B D Female sex cells (eggs) Male and Female body cells 5. Which statement is incorrect about asexual reproduction… B A Results in variation Produces genetically identical offspring (clones) C Does not involve gametes D Involves one parent 6. Which statements is incorrect… A Chromosomes are made up of genes B Genes are made up of chromosomes C Genes control the development of the characteristics of the offspring 7. Genetic engineering is used to … Create A C To B To grow human clones D Ensure that organisms have ‘desired’ or selected characteristics C 8. Cuttings are ..? B A Taken from plants to produce variation in plants Taken from plants to produce new genetically identical plants Taken from animals to produce new genetically identical animals P1 Revision The Earth and its atmosphere provide everything we need. The Earth has a layered structure. Large-scale movements of the Earth’s crust can cause changes in the rocks. It has been much the same for the last 200 million years and provides the conditions needed for life on Earth. Recently human activities have produced further changes. Earth Revision Which letter is the outer Core? D C Which letter is the inner core ? A Which letter is the Crust? B Which letter is the Atmosphere? E Which letter is the mantle? Can we accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur? A We can predict where they are likely to occur but not when B We can not predict where or when they are likely to occur Most earthquakes and volcanoes occur in predictable areas of the world along or near boundaries between tectonic plates. What are the main two metals making up the Earth’s core? … A B Gold and Steel Iron and Nickle C D Magnesium and iron Magnesium and Copper Why was crustal movement (continental drift) not generally accepted for many years after it was proposed? A B Wegener knew how but not why the continents should move apart Wegener did not know how or why the continents should move apart. Mini Plenary Match the words A, B, C and D to the numbers 1–4 in the sentences. A B C D boundaries earthquakes sudden tectonic The Earth’s 1 plates move slowly but the movement may be 2 . Volcanic eruptions and 3 occur at the 4 of the plates. (4 marks) The Earth’s crust and the upper part of the mantle are cracked into a number of large pieces called? A B C D Tinytonic Plates Tictonic Plates Tantonic Plates Tectonic Plates Mini Plenary The movement of the tectonic plates is caused by: A B C D conduction in the inner core. conduction in the outer core. convection in the mantle. radiation in the crust. 10. Tectonic plates move by a relative speed of? A B A few mm per year A few cm per year C A few m per year D A few miles per year What are the main features of a Volcano? Learning Objectives 1. State where in the World the majority of volcanoes and earthquakes occur. (D) 2. Describe how and why an earthquake occurs (B) TITLE Can we predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur? Where do most earthquakes and volcanoes occur? Most earthquakes and volcanoes occur along or near the boundaries between tectonic plates. Iceland is getting bigger. What you need to know for the exam… • Candidates should consider long-term and short-term changes in the Earth’s crust, and how these changes impact on human life. In particular, they and out about earthquakes and volcanoes – explaining them, predicting them and coping with them. • understand that earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain building generally occur at the edges of tectonic plates • Understand how the movement of tectonic plates causes earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain building, and contributes to the rock cycle What you need to know for the exam… • Can we predict earthquakes, especially those that are likely to cause most damage? • recall that earthquakes produce wave motions on the surface and inside the Earth which can be detected by instruments located on the Earth’s surface • • • • recall that earthquakes produce: a. P-waves (longitudinal waves) which travel through solids and liquids b. S-waves (transverse waves) which travel through solids but not liquids describe the difference between a transverse and longitudinal wave Predicting Earthquakes • Although we can predict where an earthquake is likely to occur, we can not predict when they will occur with any accuracy. Explain why London gets very few earthquakes. Explain why Los Angeles is preparing itself for a large earthquake. Iceland is getting wider every year by about 4 cm. The Himalayas are getting higher year by year. Using this diagram, explain how and why these plates move around on the Earth’s surface. The arrows represent convection currents. What happens at the junction of the following plates: A and F? Crust is stretched and cracks appear. In some cases magma rises up erupting as a volcano. What provides the energy for movement of the tectonic plates A magnetic forces causing movement in the mantle B movements in the mantle causing magnetic forces C heat causing radioactive processes D radioactive processes releasing heat True or False The features of the Earth’s surface were the result of the shrinking of the crust as the Earth cooled down following its formation. False Scientists once thought this was true though! Crust Forming Crust wrinkles forming mountains and valleys Cooling and Contracting The Earth 4000 million years ago. The Earth after cooling for millions of years. Higher Question Scientist once thought that the cause of many of the features was: • A expansion of the crust as it cooled down. • B expansion of the crust as it heated up. • C shrinkage of the crust as it cooled down. • D shrinkage of the crust as it heated up. The tectonic plate movements can be sudden and disastrous. Earthquakes and/or volcanic eruptions occur … C B Every where at the boundaries between A tectonic plates. at the centre of tectonic plates Write the question and answer it!!! What percentage of the Earth’s atmosphere is composed (made up of): • • • % Nitrogen % Oxygen % Carbon dioxide Learning Objectives 1. Know how the earth’s atmosphere has changed over time. 2. Know the percentages of gases in dry air. 3. Know where the noble gases are found on a periodic table. 4. Know how we use noble gases and what their properties are. How the Earth’s Atmosphere Changed? • During the first billion (1000 million) years of the Earth’s existence, there was intense volcanic activity. • Rocks decomposed, elements reacted and gases were released to form the first atmosphere. CO2 CH4 H20 NH3 The Earth’s atmosphere was originally very different from what it is today. CO2 CH4 The early atmosphere was mainly (H20) with small proportions of methane ( H 20 NH3 (C02) and )and ammonia( ). CO2 H 20 CH4 NH3 As the molten rocks on the earth’s surface down and the temperature dropped further, most of the water vapour to form , and . CO2 02 CH4 When plants appeared on the Earth, and were taken up during was produced. 02 NH3 (C02) and oxygen CO2 02 N2 As (02) collected in the atmosphere, flammable gases like methane ( ) and (NH3), burnt in this oxygen producing more (H20), and (N2). CO2 N2 02 Fossil Fuel Sedimentary Rock Over billions of years, carbon dioxide became locked up and in rocks as carbonates. as The carbon dioxide in the changing atmosphere was being removed by two processes: 1. The formation of fossil fuels from carbon compounds in plants and sea creatures. 2. The deposition of carbonates as sedimentary rocks, following erosion by rivers and from the shells and bones of sea creatures. Our Atmosphere Today • More or less the same for 200 million years! • Composed of about 80% (4/5) Nitrogen • Composed of about 20 % (1/5) Oxygen • Small proportion of other gases including carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases. The Percentages of Gases in Dry Air Pie Chart to Show the percentage of gases in dry air Gas Percentage Nitrogen 78.1 Oxygen 20.9 Argon 0.9 Carbon dioxide Neon Krypton Xenon Less than 0.1 Nobel Gases The Position of the Noble Gases (Group 0)in the Periodic Table 0 3 4 5 6 7 Noble Gases Nobel Gases • All chemically unreactive. • All colourless • All odourless • Have very low melting and boiling points • Exist as separate single atoms (other gaseous atoms exist as diatomic molecules e.g. 02, H2, N2 etc). Uses of Noble Gases • Helium is a noble gas. • Can anyone think of where Helium is used? What properties of helium make it useful in balloons and airships? Helium is used in balloons and airships because it has a low density and it is nonflammable. Uses of Noble Gases • Argon and Krypton are used in filament lamps (light bulbs) • Neon and Argon are used in electric discharge tubes to create fluorescent signs. – Neon tubes give a red colour. – Argon give a blue colour How much do you Know??? True (Thumbs Up) or False (Thumbs Down) 1. The early atmosphere was mainly carbon dioxide and methane. 2. As the Earth cooled, water evaporated. 3. The Earth’s oxygen was produced by Photosynthesis. 4. Carbon dioxide became locked up in fossil fuels and sedimentary rock. 5. Our atmosphere today contains approximately 20% oxygen. 6. The noble gases are in Group 0. 7. The noble gases are found on the far left of the Periodic table. 8. Helium is used in balloons because it is flammable. 9. Noble gases are used in filament lights and electric discharge tubes. Atmosphere Revision For 200 million years, the proportions of different gases in the atmosphere have been much the same as they are today. The atmosphere contains… A B C about about about - 20% nitrogen - 80% oxygen - small proportions of various other gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases - 80% nitrogen - 20% oxygen - no carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases - 80% nitrogen - 20% oxygen - small proportions of various other gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases Foundation Question Match the names A, B, C and D to the numbers 1 to 4 in the sentences. A B C D carbon dioxide nitrogen oxygen water vapour When the air is dry about 80% of the Earth’s atmosphere is 1 . The other 20% is mostly 2 with small proportions of the noble gases and 3 . At other times the atmosphere also contains 4 . (4 marks) C The noble gases are in which group in the periodic table. B A Group 0 Group 1 Group 2 C The noble gases are all… B A Chemically unreactive gases Chemically reactive gases Chemically unreactive solids The noble gases are used … B A in oil burning lamps and electric discharge tubes. in filament lamps and electric discharge tubes. C in filament lamps and electric dischange tubes. C The noble gases, helium is … B A much more dense than oxygen and is used in balloons. much more dense than air and is used in balloons. much less dense than air and is used in balloons. What produced the oxygen that is now in the atmosphere? A - Animals B - Plants C - Rocks Foundation Question Match the words A, B, C and D to the numbers 1–4 in the sentences. A B C D ammonia carbon dioxide oxygen water vapour After the first 1000 million years of the Earth’s existence, the atmosphere was mostly 1 . There would also have been some 2 , most of which condensed to form the oceans, plus small proportions of methane and 3 . Like the atmospheres of Mars and Venus today, there would have been little or no 4 . (4 marks) Higher Question 13 The Earth has existed for about 4500 million years. During this time the proportions of the different gases in the atmosphere has changed. Evidence from rocks and other sources is used by scientists to try to understand these changes. 13.1 Oxygen in the atmosphere has been produced: A by animals through the process of photosynthesis. B by animals through the process of respiration. C by plants through the process of photosynthesis. D by plants through the process of respiration. 13.2 Most of the carbon from the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere gradually became locked up: A in igneous rocks as carbonates and in fossil fuels. B in igneous rocks as crystals of silicates and other minerals. C in sedimentary rocks as carbonates and in fossil fuels. D in sedimentary rocks as crystals of silicates and other minerals. 13.3 A B C D During the twentieth century, the proportion of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere increased. Most scientists believe that this increase was caused by an increase in: the burning of fossil fuels. the activity of microorganisms. the photosynthesis of plants. the respiration of plants and animals. 13.4 A B C D Most scientists believe that there is a link between increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and increased global warming and that this link is: associated. causal. chance. random. (4 marks) Questions 1. Explain how argon allows you to use an electric light bulb for many hours. (2) Because there is a vacuum inside the lamp, metal atoms evaporate from the super hot tungsten filament. To reduce this evaporation and prolong the life of the filament, the bulb is filled with an unreactive gas which can not react with the hot tungsten filament. 2. Explain how neon is used for advertising.(2) The noble gases produce a coloured glow when their atoms are bombarded by a stream of electrons. The electrons come from either a high voltage discharge across the terminals of a discharge tube. Neon tubes give a red colour and argon give a blue colour.


































































![c1b revision sheet 1[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016683336_1-baea0f7acdab057d50ded8ac95b62330-150x150.png)








