* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
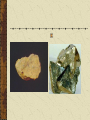
Chapter 3 Minerals Mineral Naturally occurring Inorganic Solid Definite structure – crystalline – solid in which the atoms are arranged in a repeating pattern. Definite composition Ex; Quartz - SiO2 Coal Naturally occurring Made of organic material plants Solid – non crystalline Definite composition Cubic zirconium Man made Inorganic material Solid Crystalline structure Definite composition ice quartz Hexagonal Crystal ( 6 sides) Had plenty of time and space to allow the crystal to grow Same crystal shape Formed in a tight space so you cannot see the outward appearance of a crystal Fluorite Pyrite Galena Aggregate – clumps of minerals joined together Pyrite Galena Halite Calcite- double refraction Formation of minerals 1. Cooling magma – cooling slows particles which cause them to move closer together and form compounds. - molecules arrange themselves into repeating patterns - type and amt of minerals depend on the composition of the magma - many different minerals form - quicker magma cools, faster crystals form, smaller crystal size/or no apparent crystal 2. Crystal from solution – minerals dissolved in liquids - when liquid evaporates the mineral is left behind 3. Crystals from supersaturated solution – molecules of the mineral fall out of the solution. 98% of the earth’s crust is made of only 8 elements Silicates – most common rock forming elements - minerals that contain O and Si Mineral Identification Physical properties – observable properties Hardness – how easily mineral can be scratched Talc – soft mineral -scratch with fingernail - talcum powder Diamond – hardest of all minerals - only another diamond can scratch it - used in special cutting tools Moh’s Scale of Hardness The Girls Can Flirt And Other Queer Things Can Do 1. talc 2. gypsum 3. calcite 4. fluorite 5. apatite 6. feldspar (orthoclase) 7. quartz 8. topaz 9. corundum 10. diamond Luster How light is reflected from a mineral’s surface Metallic – shines like metal Nonmetallic luster Nonmetallicglassy, dull, pearly, Silky Earthy Greasy Color Can’t be depended upon because some minerals have a variety of colors Some minerals have the same color Chalcopyrite – left Gold nugget - below Streak Powdered form of a mineral Rub the mineral across a piece of unglazed porcelain Left – hematite Right - pyrite Graphite Streak – black to gray Hardness – 1 Feels – greasy Luster – metallic Opal No streak Hardness 5-6 Luster – waxy Fracture and Cleavage Cleavage – when a mineral breaks along smooth flat surfaces Fracture – minerals that break with rough or jagged edges Conchoidal – circular pattern in break irregular Other Properties Magnetic Double images Taste – halite/salty Smell – sulfur – smells like rotten eggs Reaction to HCl – bubbles. Fluoresence'