* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 – Plate Tectonics
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
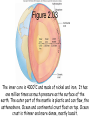
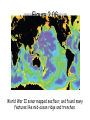
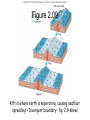
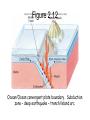
Chapter 2 – Plate Tectonics Part 1 er 2 The Sea Figure 2.01 71% of the earth’s surface is water. Two thirds of earth’s crust is in the northern hemisphere. 80% of the southern hemisphere is ocean. Figure 2.02 Traditionally four ocean basins; Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Artic but one real ocean. The water that surrounds antarctica is referred to as the southern ocean. connected to the oceans are Mediterranean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and South China Sea. Early earth was molten and the densest material was pulled to the center of the earth by gravity. differentiation The earth slowly cools, thin crust hardens and water condenses into liquid. The earth just happens to be the right distance from the sun. No water no life! Figure 2.03 The inner core is 4000°C and made of nickel and iron. It has one million times as much pressure as the surface of the earth. The outer part of the mantle is plastic and can flow, the asthenoshere. Ocean and continental crust float on top. Ocean crust is thinner and more dense, mostly basalt. Figure 2.04 Once world map started taking shape, scientists noticed that Africa and South America fit together like puzzle pieces. Coincidence? Alfred Wegener hypothesised that continents drifted apart. 1960’s geologists agree the continents do move. Plate tectonics Figure 2.05 Earthquakes indicate plate boundaries. Figure 2.06 World War II sonar mapped seafloor, and found many features like mid-ocean ridge and trenches. Figure 2.07 Deep earthquakes indicate crust is being destroyed and shallow earthquakes indicate seafloor spreading. Figure 2.08 Magnetic reversal shows newest crust is in the middle of the ocean. Figure 2.09 Rift is where earth is seperating, causing seafloor spreading – Divergent boundary- fig. 2.9-Know! Figure 2.10 Earthquakes indicate plate boundaries Figure 2.11 Ocean/Continental convergent plate boundary. Subduction zone – deep earthquake – trench/mountains Figure 2.12 Ocean/Ocean convergent plate boundary. Subduction zone – deep earthquake – trench/island arc. Figure 2.13 Mount Veniaminof - Aleutian Island Arc