* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Subduction Zones
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
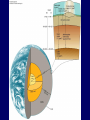
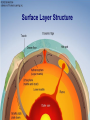
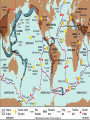
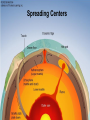
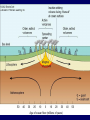
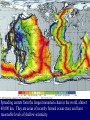
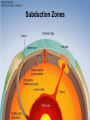
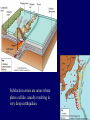
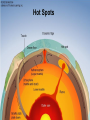
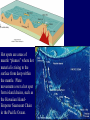
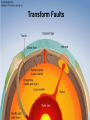
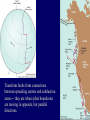
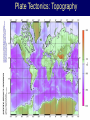
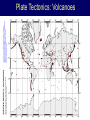
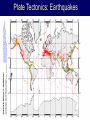
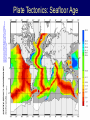
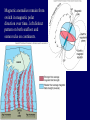
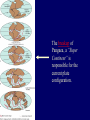
Earth Structure • Basic layers • Layered surface structure • Spreading centers • Subduction zones • Hot Spots • Transform faults • Evidence • Animations Surface Layer Structure All plate motions can be described by thinking about the movement of plates on a sphere. Spreading Centers Spreading centers form the longest mountain chain in the world, almost 60,000 km. They are areas of recently formed ocean crust, and have reasonable levels of shallow seismicity. Subduction Zones Note that Earth is density stratified, that is, each deeper layer is denser than the layer above. At the Peru-Chile Trench, the oceanic lithosphere is much denser than the continental lithosphere, so it sinks down into the mantle Subduction zones are areas where plates collide, usually resulting in very deep earthquakes. Ocean islands and basins can both be created and destroyed. Destruction occurs when two pieces of continental lithosphere or island arc collide: they accrete to each other and the basin between is destroyed. This process also brings old seafloor (ophiolites) up onto continent edges. Hot Spots Hot spots are areas of mantle “plumes” where hot material is rising to the surface from deep within the mantle. Plate movements over a hot spot form island chains, such as the Hawaiian IslandEmperor Seamount Chain in the Pacific Ocean. Transform Faults Transform faults form connections between spreading centers and subduction zones -- they are where plate boundaries are moving in opposite, but parallel directions. Pacific NW has it all! • 5 plates • Subduction zones • Spreading center (JdF Ridge) • Transform faults • Ophiolites (Olympics) • Deep & shallow earthquakes • Subduction volcanoes • NEPTUNE - proposed regional cabled observatory - see http://www.neptune.washington.edu Plate Tectonics: Topography Plate Tectonics: Volcanoes Plate Tectonics: Earthquakes Plate Tectonics: Seafloor Age Magnetic anomalies remain from switch in magnetic polar direction over time...left distinct pattern on both seafloor and some rocks on continents. The Integrated Picture The breakup of Pangaea, a “Super Continent” is responsible for the current plate configuration. Plate Motions through time