* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Origin and Early Evolution of Life
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
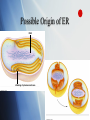
The Origin and Early Evolution of Life Biology 1010 The Big Bang 12-15 billion years ago all matter was compressed into a space the size of our sun Sudden instantaneous distribution of matter and energy throughout the known universe Archaean Eon and Earlier 4,600 mya: Origin of Earth 4,600 - 3,800 mya (about 800 million years) Formation of Earth’s crust, atmosphere Chemical and molecular evolution First cells (anaerobic bacteria) Earth Forms About 4.6 and 4.5 billion years ago Minerals and ice orbiting the sun started clumping together Heavy metals moved to Earth’s interior, lighter ones floated to surface Produced outer crust and inner mantle First Atmosphere Hydrogen gas Nitrogen Carbon monoxide Carbon dioxide No gaseous oxygen Earth Is “Just Right” for Life Smaller in diameter, gravity would not be great enough to hold onto atmosphere Closer to sun, water would have evaporated Farther from sun, water would have been locked up as ice Stanley Miller’s Experiment Mixed methane, hydrogen, ammonia, and water Simulated lightning Amino acids and other small molecules formed electrodes to vacuum pump CH4 NH3 H2O H2 spark discharge gases water out condenser water in water droplets boiling water water containing organic compounds liquid water in trap Animation How Did Cells Originate? In the first 600 million years or so of Earth history, enzymes, ATP, and other crucial organic compounds probably assembled spontaneously Possible Sequence membrane-bound proto-cells living cells self-replicating system enclosed in a selectively permeable, protective lipid sphere DNA RNA formation of protein-RNA systems, evolution of DNA enzymes and other proteins formation of lipid spheres spontaneous formation of lipids, carbohydrates, amino acids, proteins, nucleotides under abiotic conditions RNA World DNA is genetic material now DNA-to-RNA-to-protein system is complicated RNA may have been first genetic material RNA can assemble spontaneously How switch from RNA to DNA might have occurred is not known The First Cells Originated in Archaean Eon Were prokaryotic heterotrophs Secured energy through anaerobic pathways No oxygen present Relied on glycolysis and fermentation Proterozoic Eon Origin of photosynthetic eubacteria Oxygen accumulates in atmosphere Origin of aerobic respiration Advantages of Organelles Nuclear envelope may have helped to protect genes from competition with foreign DNA ER channels may have similarly protected vital proteins Possible Origin of ER DNA infolding of plasma membrane Theory of Endosymbiosis Lynn Margulis Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the descendents of free-living prokaryotic organisms Prokaryotes were engulfed by early eukaryotes and became permanent internal symbionts http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/anis amples/nonmajorsbiology/organelles.html Evolutionary Tree hydrogen-rich anaerobic atmosphere atmospheric oxygen, 10% archaean lineage ancestors of eukaryotes endomembrane system and nucleus cyclic pathway of photosynthesis origin of prokaryotes 3.8 billion years ago noncyclic pathway of photosynthesis aerobic respiration 3.2 billion years ago 2.5 billion years ago Evolutionary Tree