* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
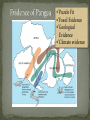
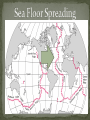
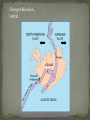
Objective Warm-Up: You will use the theory of What do you know plate tectonics and the changes in the earth’s surface in order to explain the evidence for continental drift theory. about the theory of plate tectonics? How do plates move? The theory that the Earth’s Crust and upper mantle (Lithosphere is broken up into 20 MOVING sections called plates. Greek – “tektonikos” of a builder Pieces of the lithosphere that move around Each plate has a name Fit together like jigsaw puzzles Plates Float on top of the asthenosphere similar to ice cubes in a bowl of water http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/unanswered.html “Plates” of lithosphere are moved around by the underlying hot mantle convection current Hot material rises while, cooler material sinks Created by the uneven heating of the asthenosphere “It is only by combing the information furnished by all the earth sciences that we can hope to determine “truth” here.” -Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) Alfred Wegener 1915 Continents were once a single land mass that drifted apart. Fossils of the same plants and animals are found on different continents Called this supercontinent Pangea, Greek for “all Land” Split again – Laurasia & Gondwanaland 180 million years ago http://members.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/planets/earth/Continents.shtml Puzzle Fit Fossil Evidence Geological Evidence Climate evidence Some thing to think about: What did Wegener propose as a method of explaining the close fit of the continents on either side of the Atlantic Ocean? What was so unusual about the fossil remains of Mesosaurus? How did clues found in South Africa and Arctic islands support Wegener's theory of continental drift? Why wasn't Wegener's theory accepted at the time? Is the Hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single land mass, broke up and drifted to their present locations. Wegener Evidence: There are 4 pieces: 1. 2. 3. 4. What evidence did Wegner have that that the continents use to be one large land mass called Pangaea? How does the movement from Pangaea impact the location of some of the resources we use today? (think of coal and the conditions necessary for it to form) • Mid-Ocean Ridge : underwater mountain chains that run through the Earth’s Basins • Magma rises to the surface cools and new crust forms (Basalt) • Older Crust is pushed farther away from the ridge http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html http://www.geology.com http://www.geology.com http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com www.geology.com Name the 3 main layers of the Earth What is a tectonic plate? What was Pangea? What is Sea-Floor spreading? Name the three different types of plate boundaries and one location on Earth for each one