* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Deforming the Earth`s Crust: Faulting
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
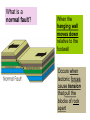
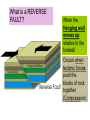
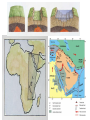
Pg. 129 Deforming the Earth’s Crust: Faulting What is a FAULT? When rock layers BREAK when stress is applied One block of rock slides relative to another What is the hanging wall, Narrow base block of angled crust see page 114 the foot wall? Broad base block of angled crust What is a normal fault? When the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall Occurs when tectonic forces cause tension that pull the blocks of rock apart A normal fault What is a REVERSE FAULT? When the Hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall Occurs when tectonic forces push the blocks of rock together (Compression) A reverse fault What are STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS? Form when opposing forces cause rock to break and move horizontally Example: California’s San Andreas fault A strike slip fault Geologic Activity, http://www.nps.gov/pore/naturescience/geologicactivity.htm Mountain Building • Occurs because of tectonic plate movement What are folded mountains? Rock layers that are squeezed together Form at convergent plate boundaries Make the highest mountains in the world Folded mountain Layers that are squeezed together What are some examples of folded mountains? Appalachian mountains The Alps Himalayan Mountains What are fault block mountains? Tension causes large blocks of rock to drop down Example: Teton Mountains, Wyoming Fault block mountains Grand Tetons Wyoming Volcanic Mountains What is uplift and subsidence? Subsidence—the sinking of a region of the Earth’s crust Uplift—the rising of a region of the Earth’s crust What is Tectonic Letdown? Sinking of a region of Earth due to tension Rift zone – a set of deep cracks that form between two plates that are pulling apart Formation of a Rift Valley Sequence showing how movements deep under the Earth's Crust help to create a Rift Valley