* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside Earth Ch. 2 Sec. 1 Notes
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
3D fold evolution wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
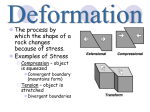
Ch. 2 Sec. 1 Notes Forces in Earth’s Crust *The movement of Earth's plates causes stress on the rocks Stress: A force that acts on rocks to change its shape or volume -Stress adds energy to rock -Energy is stored until rock changes shape or breaks 3 Types of Stress 1. Tension -Pulls on the crust stretching it so it is thinner in the middle -Occurs where plates move apart 2. Compression -Squeezes rock until it folds or breaks -Occurs where plates come together 3. Shearing -Pushes a mass of rock in 2 opposite directions -Occurs where plates slide past each other *When enough stress builds up in the rocks, the rocks break and create a fault -Most faults occur along plate boundaries 3 Types of Faults 1. Normal Fault -Caused by tension in the crust (move apart) -1 rock lies above the fault (hanging wall) and the other below the fault (footwall) 2. Reverse Fault -Caused by compression (come together) 3. Strike-Slip Fault -Caused by shearing (move past each other) Changes in Earth’s Landforms *The forces of plate movement can fold, stretch, and uplift the crust creating visible landforms* 1. Anticline: a fold in rock that bends upward into an arch 2. Syncline: a fold in rock that bends downward into a valley 3. Folded mountains: mountains created by anticlines and synclines 4. Fault-block mountains: mountains created when 2 normal faults cut through a block of rock 5. Plateaus: a large area of flat land elevated high above sea level