* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Continental Drift and Sea Floor Spreading Notes
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
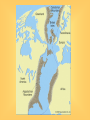
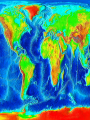
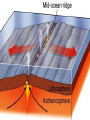
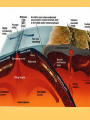
Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Pop Quiz 1) What was the name of the scientist that developed the idea that the continents had been once joined together in one land mass? 2) What was the name given to supercontinent that once existed? 3) The idea that the continents have slowly shifted over time is know as ________. 4-5) Give two pieces of evidence used to support this theory. 6) Why was his theory rejected? Plate Tectonics Pop Quiz 1) What was the name of the scientist that developed the idea that the continents had been once joined together in one land mass? Alfred Wegener 2) What was the name given to supercontinent that once existed? Pangaea 3) This idea that the continents have slowly shifted over time is know as ________. continental drift Plate Tectonics Pop Quiz 4-5) Give two pieces of evidence used to support this theory. -fossil evidence -coal fields match up -climate change/tropical fossils found in Arctic regions -mountain ranges line up -continents fit like a puzzle 6) Why was his theory rejected? -Wegener could not prove “how” or what force caused the continent to move The Plate Tectonics 2 Column Notes – Guiding Questions 1) Who was Alfred Wegener and what was his theory? 2) What are pieces of evidence to support Wegener’s theory? 3) Why was Wegener’s theory rejected? 1) Who was Alfred Wegener and what was his theory? - 1915, German Scientist -developed idea of continental drift -position of continents have shifted - one large land mass existed about 300 million years ago -Pangaea (“all the earth/all lands”) -over next 100 million years Pangaea started to break apart 2) What evidence was used to support his theory? -continents fit together like a puzzle (Africa and South America) -matching rock layers at the edge of the continents -mountain ranges line up 2) What evidence was used to support his theory? Evidence to support Wegener’s theory – -fossil evidence on both continents (Mesosaurus) -coal fields line up across continents -glacial evidence in South America (scratches on rocks) 3) Why was Wegener’s theory rejected? -he could not prove “how” the continents moved -could not identify what force pushed continents together or pulled them apart *Wegener also had to change ideas about how mountains formed Plate Tectonic Notes – Continued pages 141-147 4) What is sonar? (2 facts) 5) What is the mid-ocean ridge? (3 facts) 6) What is Sea-Floor Spreading (4/5 facts) -try to describe the process 7) What evidence of sea floor spreading exists? (try to define/describe each of them) 4) What is sonar? sonar - a device that bounces sound waves off underwater objects and record their echoes - 1950-1960’s – sonar technology allowed scientists to map the ocean floor *animation. 5) What is the mid-ocean ridge? mid-ocean ridge – -underwater mountains -connect all along the ocean floor (like seams on a baseball) -form the largest mountain chain in the world -example: Mid-Atlantic Ridge 6) What is sea floor spreading? sea floor spreading – -the sea floor spreads apart along both sides of a mid-ocean ridge, forming a “crack” -lava erupts from the crack, then cools and hardens on each side of the ridge -new strips of the ocean floor form along both sides -the newly formed oceanic crust moves away from the crack in the ridge *animation* 7) What evidence of sea floor spreading exists? 1) molten material -along the mid-ocean ridge molten material erupts -it quickly cools and hardens and looks like pillows or squeezed toothpaste *video 7) What evidence of sea floor spreading exists? 2) magnetic stripes -the ocean floor is in a pattern of magnetized stripes -the stripes match up on opposite sides of the mid-ocean ridge -a record of the Earth’s magnetic field changing on both sides of the mid-ocean ridge *animation* 7) What evidence of sea floor spreading exists? 3) drilling samples -rock samples were taken on both sides of the mid-ocean ridge -the farther away from the ridge, the older the rock samples 8) What is an ocean trench? deep ocean trench -a place where part of the ocean floor sinks back into the mantle 9) What is subduction at an ocean trench? subduction -the actual process of the ocean floor sinking back into the mantle -sea-floor spreading and subduction work together moving the ocean floor like a giant conveyor belt -ocean floor is recycled and renewed every 200 million years 10 ) What is the theory of Plate Tectonics? Plate Tectonics Theory – -the Earth’s lithosphere, is broken into several large slabs, called plates. -these plates are slowly moving around the planet. This theory explains – -why continents move -how mountains form -how volcanoes form -why earthquakes occur 10 ) What is the theory of Plate Tectonics? -links together the theories of continental drift and sea-floor spreading -explains how the Earth has evolved over time -explains the formation, movements, collisions and destruction of the Earth’s crust Major Plates: -Pacific -Eurasian -African -North American -South American -Antarctic North American Eurasian Eurasian Juan de Fuca Philippine Pacific Arabian Cocos IndoAustralian Caribbean Nazca African South American Scotia Antarctic Indo- Austr Plate Tectonics -3 types of boundaries -divergent -convergent -transform Plate Tectonics divergent boundary – where plates move apart (divide) “constructive” – land is being created What happens/develops: -sea floor spreading -mid ocean ridge Examples: -Mid-Atlantic Ridge -East African Rift in Red Sea convergent boundary –where plates move toward each other (come together) “destructive” – land is being destroyed What happens/develops: -large mountain ranges -trenches -subduction -earthquakes and volcanic eruptions Examples: Himalaya’s – Indo-Australian plate colliding with Eurasian plate transform boundary – plates slide past each other What can happen: -earthquakes occur Example: San Andreas Fault, CA Review video link