* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 Test Review Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
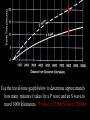
Chapter 10 Review Place these notes in your Notebook. The deepest earthquakes tend to occur at subduction boundaries. The part of a seismograph that does not move during an earthquake is the pen. A minimum of 3 seismograph stations is needed to locate an epicenter. One seismograph station, by itself, can determine the distance to the epicenter. The Richter scale measures earthquake magnitude. The Mohorovicic discontinuity named after Andrija Mohorovicic, occurs between the crust and the mantle. A boundary between dense rocks 50 km below the surface, and shallower, less dense rocks. Buildings on bedrock survive earthquakes better than buildings on soil. Soils under buildings may settle from severe shaking. Some soils under buildings become liquefied due to severe shaking. An earthquake with Richter magnitude 8 releases 961 times more energy than an earthquake with Richter magnitude 6. In an earthquake’s shadow zone neither P waves nor S waves from the earthquake are received. Strain that builds up along faults at or near plate boundaries is the cause of most major earthquakes. P waves, also called primary waves, can travel through any material, and squeeze and stretch rock materials. Some surface waves cause particles of rock to move from side to side. Most modern seismograph stations have equipment that records up-and-down motions, north-south side-to-side motions, and east-west side-to-side motions. There may be as many as 100 aftershocks in a day after an earthquake. Aftershocks can cause damage to buildings. Aftershocks are usually not as strong in magnitude as the initial earthquake. Which one is more seismically active? Chicago, Illinois Syracuse, New York New Madrid, Missouri Clermont, Florida The New Madrid earthquakes of 1811 and 1812 occurred far from a plate boundary. The location of the foci of earthquakes that have occurred in the past along the fault would help scientists identify where a seismic gap may exist along a fault. The fact that the outer core is a liquid has been concluded and is supported by studies of earthquake waves passing through Earth. Liquefaction would be most likely to occur in loose sediments. The transition zone separates the upper mantle from the lower mantle. Use the travel-time graph below to determine approximately how many minutes it takes for a P wave and an S wave to travel 8000 kilometers. P wave = 12 min S wave =20 min Essay: Explain how scientists could use seismograph station data to locate the epicenter of an earthquake. To locate the epicenter of an earthquake, scientists use data from three seismograph stations. A reading from each station is used to determine the distance of the epicenter from the station. A circle is drawn whose radius is this distance. Three circles are drawn, one for each seismograph station. The point at which all the circles intersect is the epicenter. Essay # 2 Describe some measures that can be taken to decrease damage from earthquakes. Earthquake-prone regions should have procedures to handle earthquakerelated emergencies. In addition, implementing building codes derived form scientific measurements can help create buildings that can withstand the shaking.