* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 2 Worksheet - OG
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
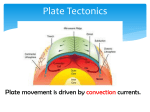
Lesson 2 Worksheet Seafloor Spreading What is seafloor spreading? 1. What forms basalt? Lava that cools and solidifies 2. Which type of rock forms oceanic crust? Basalt 3. What happens to old oceanic crust as new oceanic crust forms? New crust pushes old crust away from the ridge 4. What happens to the density of rock as it cools It becomes more dense 5. Where does the crust move as it becomes denser? Away from the mid-ocean ridge 6. Which force draws the cooler, denser crust downward and away from the ridge? Gravity 7. What is formed when lava cools and crystallizes on top of the oceanic crust? Basalt (sediment) 8. Where is seafloor sediment thickest? Far away from mid-ocean ridge 9. What shape does the seafloor take where sediment is the thickest? Smooth plain 10. What is this area of the seafloor called? Abyssal plain 11. What is the ocean crust always doing? Spreading 12. What happens as the ocean crust spreads? Continents move! 13. What does the crust record as it cools? Direction of Earth’s magnetic field 14. What does basalt contain that makes this possible? Iron-rich minerals 15. What forms when Earth’s magnetic field changes direction? Magnetic stripes on ocean floor 16. What do magnetic stripes confirm? Ocean crust is made at mid-ocean ridge and is carried away from ridges as magma flows upward and out as lava What evidence is used to support seafloor spreading? 1. What does normal polarity mean? It means that magnets point north. 2. What does reversed polarity mean? Changes direction and magnets point south 3. How can scientists tell when changes occur in Earth’s magnetic field? Minerals give a magnetic signature that will point either north or south. 4. How often do magnetic reversals occur? Every few hundred thousand (100,000) years to a few million (1,000,000) years 5. What do Earth’s magnetic stripes indicate about ocean crust? New ocean crust is found at mid-ocean ridges and older crust is further away. 6. How do Earth’s magnetic signatures support the idea that continents move? It shows that crust is moving and the seafloor is spreading.