* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FOLDS AND STRUCTURES DUE TO FOLDING
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
TaskForceMajella wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Paleostress inversion wikipedia , lookup
3D fold evolution wikipedia , lookup
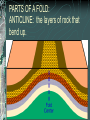
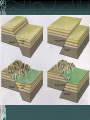
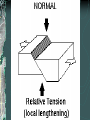
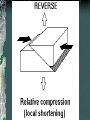
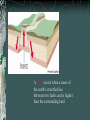
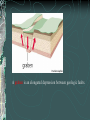
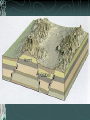
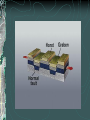
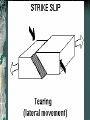
FOLDS AND STRUCTURES DUE TO FOLDING Folding generally takes place in areas of sedimentary rocks that have been laid down in horizontal layers called strata. When compression produces thrust [convergence], the earth folds along lines of strength and weakness. This creates long ranges of FOLD MOUNTAINS – Alps, Himalayas, Rockies… The Alps Compressed into folds PARTS OF A FOLD: ANTICLINE: the layers of rock that bend up. ANTICLINE SYNCLINE: The layers of rock that bend down SYNCLINE SYNCLINE Anticline Anticline(s) Faulting – adjacent surfaces are displaced relative to one another Normal Fault In normal faulting, the hanging wall block moves down relative to the footwall block. Normal faults are associated with crustal TENSION. Normal Fault… Reverse Fault In reverse faulting, the hanging wall block moves up relative to the footwall block. Reverse faults are associated with crustal COMPRESSION and are also known as thrust faults. Components of FAULTING… A horst occurs when a mass of the earth's crust that lies between two faults and is higher than the surrounding land. A graben is an elongated depression between geologic faults. Strike-slip Fault In strike-slip faulting, the two blocks move either to the left or to the right relative to one another.