* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
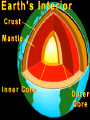
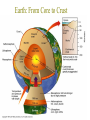
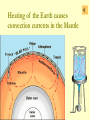
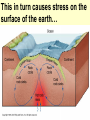
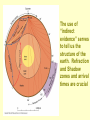
The Earth: A Vibrant Planet Sorry to break it to you but the earth is NOT round – rather a spheroid. It bulges at the equator and flattens at the poles… Structure of the Earth Earth: From Core to Crust THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH: CRUST – earth’s exposed rock MOHO the separation between the crust and the asthenosphere ASTHENOSPHERE – Plastic like substance – responsible for movement of earth’s crust. MANTLE (MESOSPHERE) a semi-liquid plastic consistency which liquefies when pressure is reduced OUTER CORE liquid INNER CORE solid Heating of the Earth causes convection currents in the Mantle This in turn causes stress on the surface of the earth… We know the structure of the earth due to the study of SEISMOLOGY (the study of earthquake waves) • the branch of geology that studies earthquakes •Primary (P) waves and Secondary (S) waves pass through the internal layers of the planet Primary Waves • P waves stretch and squeeze; moving quickly, can pass through any material • Travel by compression through solids, liquids, and gases • Speed up through the mantle • Drop at the outer core (liquid) • Speed up at the inner core (solid) Secondary Waves • S waves vibrate passing only through solids • Slower than the P wave (60% of the speed) • Will NOT travel through liquid • Speeds up gradually through the mantle • Then stops at outer core Waves in Action The use of “indirect evidence” serves to tell us the structure of the earth. Refraction and Shadow zones and arrival times are crucial Our Vibrant Earth A Sombrio Production