* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interior of Earth
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Earth’s Interior
{
How do you measure something you can’t observe
directly?
Newton
300 years ago, Isaac Newton
used observations of the planets
and his law of gravity to
calculate that the density of the
Earth was double that of the
surface rocks.
His density value is essentially
unchanged today.
Great hair. Greater scientist.
Therefore, since 1700 we have known that the
interior of the Earth was composed of different
material to the crust.
We now differentiate the interior into two types
of mantle (asthenosphere and lower mantle)
and two types of core (outer and inner).
The key to measuring the size of each of these
regions is the study of seismic waves.
Differentiation
By chemical
composition
(what it’s
made of):
By physical
properties
(density, state of
matter, etc.):
• Crust
1. Continental
crust
2. Oceanic crust
3. Asthenosphere
(plastic part of
upper mantle)
4. Lower mantle
5. Outer Core
6. Inner Core
• Mantle
• Core
Two ways to divide into layers
Waves change speed when they pass from one
medium to another. Why? Well, look at this
lawnmower:
Refraction
P-waves
S-waves
Faster
Slower
Longitudinal /
Compression
Transverse
Pass through
all states of
matter
Only pass
through solids
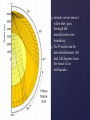
Seismic waves refract
when they pass
through the
mantle/outer core
boundary.
No P-waves can be
detected between 104
and 140 degrees from
the focus of an
earthquake.
Why can’t we detect
any P-waves in the
shadow zone?
Why can we detect Pwaves opposite the
earthquake focus?
Attenuation
S-waves aren’t
completely blocked by
the outer core, they are
attenuated. This means
they gradually fade to
nothing.
Another example:
sunlight is attenuated
by sunglasses.
So only P-waves are
detected on the
opposite side of the
Earth.