* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Volcano (1997 film) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
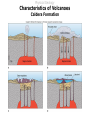
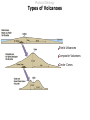
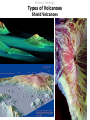
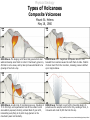
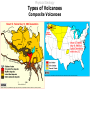
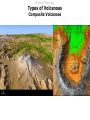
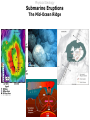
Lecture 5 Volcanism Physical Geology Lecture Outline I II A) B) C) III IV V VI Characteristics of Volcanoes Types of Volcanoes Shield Volcanoes i. ii. iii. Description Composition Eruption Features i. ii. iii. iv. Description Composition Eruption Features Distribution i. ii. iii. Description Composition Eruption Features Composite Volcanoes Cinder Cones Lava Floods Submarine Eruptions Living with Volcanoes Conclusions Physical Geology Characteristics of Volcanoes Vent Fumarole Crater Caldera Volcanic Domes Physical Geology Characteristics of Volcanoes Vents and Fumaroles vent : the opening at the earth's surface through which volcanic materials are extruded. fumarole : a hole or vent from which volcanic fumes or vapors issue. Physical Geology Characteristics of Volcanoes Craters crater : a basin-like rimmed structure at the top or on the flanks of a volcanic cone; it is formed by explosion or collapse Mt Erebus, Antarctica Halemaumau, Hawaii Mt Poas, Coast Rica Physical Geology Characteristics of Volcanoes Calderas Aniakchak, Alaska caldera : a large basin-shaped volcanic depression, more or less circular. the diameter of which is many times greater than that of the included vent or vents, irrespective of the steepness of the walls or the form of the floor. Kaguyak, Alaska Crater Lake, Oregon Physical Geology Characteristics of Volcanoes Caldera Formation Physical Geology Characteristics of Volcanoes Volcanic Dome volcanic (lava) dome: steep-sided mound built by magma too viscous to flow far from vent before crystallizing and cooling. Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Shield Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Cinder Cones Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Shield Volcanoes o Slope: Gentle (2-10 ) Height: up to 10 km Composition: Flow layers Basaltic Eruption: Effusive Low-Viscosity Lava A'a Pahoehoe Flank Eruptions Other Characteristics: Lava Ponds and Tubes Spatter Cones Mauna Loa, Hawaii Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Shield Volcanoes Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Shield Volcanoes pahoehoe a'a Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Shield Volcanoes lava tube : a hollow space beneath the surface of a solidified lava flow, formed by the withdrawal of molten lava after the formation of a surficial crust spatter cone: A low steep-sided cone of spatter built by lava fountains along a fissure or around a vent Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes o Slope: < 33 Height: 1000 - 4000 m Composition: Layers of pyroclastic fragments and lava flows Andesitic Eruption: Explosive Other Characteristics: Magma blocks conduit Glowing clouds Mt St Helens and Mt Ranier Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Mount St. Helens May 18, 1980 8:32:00 a.m. The bulging north flank that geoscientists had watched develop since March is intact. It had clearly grown by 450 feet in some areas, and by late April was estimated to be growing at five feet a day. 8:32:10 a.m. A 5.1 magnitude earthquake about 1 mile beneath the mountain causes the north flank to slide. Tendrils of steam burst from the mountain, releasing pressure bottled up in magma below. 8:33:00 a.m. A cubic mile of mountain gives way, traveling at 70 to 150 mph, and superheated rocks in the volcano's core are suddenly exposed, shooting a lateral blast of gas north, incinerating everything in its path. Huge glaciers on the mountain's peak melt instantly. 8:33:20 a.m. The blast is over but the mountain begins to pulverize as the eruption vents its full fury, sending a thick, 3mile-wide ash cloud 80,000 feet into the sky. http://seattlepi.nwsource.com/mountsthelens/grapherupt.shtml Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes http://www.3dnworld.com Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Physical Geology Types of Volcanoes Cinder Cones o Slope: Steep (33 ) Height: < 300 m Composition: Pyroclastic fragments Various Eruption: Explosive Other Characteristics: Short-lived Paricutin, Mexico Cinder Cone,Mauna Kea, Hawaii Physical Geology Lava Floods Physical Geology Lava Floods The Columbia Plateau Physical Geology Submarine Eruptions Kavachi, Solomon Islands Physical Geology Submarine Eruptions The Mid-Ocean Ridge Physical Geology Volcanic Hazards