* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Catastrophic Event
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
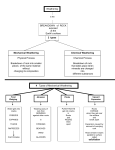
Chemical Weathering the weathering of a rock surface through chemical processes such as oxidation, solution, and hydrolysis Different effects of chemical weathering according to rock type: limestone in foreground; granite in left background, Vermont. Contaminant • A substance that is either present in an environment where it does not belong or is present at levels that might cause harmful • a low triangular area of alluvial deposits where a river divides before entering a larger body of water Deposition • the natural process of laying down a deposit of something Drought • A long period of abnormally low rainfall, especially one that adversely affects growing or living conditions. Dune •a hill of sand built by aeolian processes Earthquake • shaking and vibration at the surface of the earth resulting from underground movement along a fault plane of from volcanic activity Ecology • is the scientific study of the relation of living organisms to each other Ecological Succession • a process of ecological change in which a series of natural communities are established and then replaced over time Erosion • the process of weathering and transport of solids (sediment, soil, rock and other particles) in the natural environment Fertilizer • substances that supply plant nutrients or amend soil fertility Flood • an overflow of an expanse of water that submerges land Groundwater • water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations Mechanical Weathering • when rocks are broken down without any change in the chemical nature of the rocks Runoff • the movement of landwater to the oceans, chiefly in the form of rivers, lakes, and streams. Primary Succession • the gradual growth of organisms in an area that was previously bare Secondary Succession • the series of community changes which take place on a previously colonized, but disturbed or damaged habitat Surface Water • water collecting on the ground or in a stream, river, lake, wetland, or ocean Tornado • a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud Tsunami • caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, usually an ocean, but can occur in large lakes Volcano • an opening, or rupture, in a planet's surface or crust, which allows hot magma, ash and gases to escape from below the surface Watershed • the area of land where all of the water that is under it or drains off of it goes into the same place Weathering • the breaking down of Earth's rocks, soils and minerals through direct contact with the planet's atmosphere Wildfire • any uncontrolled fire in combustible vegetation that occurs in the countryside or a wilderness area Catastrophic Event • a sudden and widespread disaster