* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
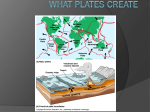
At mid-oceanic ridges, basaltic magma forms by decompression melting of rising mantle rock. Some magma intrudes upward through dikes and erupts in the rift zone. Seawater is heated as it circulates through the hot crust and causes extensive hydrothermal alteration, metamorphosing large volumes of basalt. Much of the oceanic crust and its topographic features are related to igneous activity. Rocks of the ocean crust have not been deformed by strong compression: simple structure in contrast to the complex structure of the continents. All oceanic crusts are less than 200 million years old. Abyssal hills are the most abundant landforms on Earth: 30% of ocean floor: these are elongated asymmetrical, steep-sloped hills, along rifts. There is continuous volcanic activity. This represents the initial stages of the formation of ocean basin. The region is undergoing extension at the rate of 0.5cm/y. At Afar Lowlands the rift has a very thin crust (8km): the rifting of the crust is nearly complete and basalt volcanoes are abundant. The Red Sea Rift is 3000 km long and 100 - 300 km wide. The floor is made of thin continental crust - thinned by extension and normal faulting. There is a symmetrical magnetic anomaly in the central part of Red Sea. Continental rifting occurs when divergent plate margins develop in continents. They are typified by normal faulting, shallow earthquakes, basaltic and rhyolitic magmatism. Many rift valleys are closed depressions and have been filled with water to form freshwater lakes. There are sedimentary rock sequences (fluvial and lacustrine) as well as evaporites (because of the high evaporation rates) along with volcanic rocks within the rift valleys - in contrast to mid-oceanic Read pages 528 - 530 of Hamblin: Plate movement during the last 200 million years for a short history of the evolution of the Earth’s present structure. Prepare your own timeline of the changes in the configuration of the Earth’s crust through the geological ages.