* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
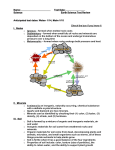
Chapter 12 Environmental Geology, Processes, Minerals & Soils Geology • Geology is the study of the Earth’s dynamic process with respect to it’s interior and surface structure and features. Rocks, minerals, chemicals, earthquakes, and volcanoes are studied to reveal information about our planet. • Review the handout from Chapter 6 on the geosphere. Geosphere • Core – central, innermost part of the Earth with a solid part surrounded by hot, liquid molten material • Mantle – thick solid region that surrounds the core and has zones of molten rock that flows (asthenosphere) • Crust – thin, outermost region of the geosphere **Note that the lithosphere is composed of the upper mantle and the crust! Plate Tectonics • Tectonic plates – constant movement of the rigid plates due to heat (energy) flow of materials • Plate tectonics is the theory that explains the movement of the plates and the processes that occur at their boundaries • Plate motion has produced mountains, ocean ridges, trenches and other features – Plate movement provides many minerals we use as resources – Continental drift helps to explain migration and evolutionary patterns Global Geological Information • Internal process that occur under the Earth’s surface • See figure 12-3 (a) for a map of earthquakes and volcanoes along bands on the earth • See figure 12-3 (b) for a map of plate boundaries Plate Boundaries • Divergent plate boundaries – plates move in opposite directions • Convergent plate boundaries – plates move toward each other • Transform faults – plates that slide past each other Erosion & Weathering • External process that happen on the Earth’s surface • Erosion is the process where matter is dissolved, loosened or worn away from one place to another (ex. streams) • Weathering is the mechanical or chemical process that provides change to the surface matter – Mechanical – physical changes (ex. frost wedging) – Chemical – decompose by reaction (ex. acid rain) Rocks • Minerals – elements & inorganic compounds that occur naturally (ex. gold) • Rocks – large continuous part of the earths crust & many consist of 2 or more minerals • Rock types – 3 broad classifications are: – Igneous – formed from molten rock (ex. lava) – Sedimentary – impaction of sediment (ex. shale) – Metamorphic – rock that has been subjected to high temperature, high pressure, chemical activity or a combination of these (ex. marble) Rock Cycle • The rock cycle is the interaction of processes that continuously change rocks over time – Recycles materials over millions of years – Slowest of all Earth’s cycling processes – Concentrates the Earth’s non-renewable resources Mineral Resources • Non-renewable resources – mineral resources that take millions to billions of years to occur • Ore is mineral resources mined for profit – Metallic mineral – ex. iron & copper – Nonmetallic mineral – ex. salt & clay – Energy resources – ex. coal & oil USGS Mineral Catagories • The USGS has 4 classifications for non-renewable mineral resources – Identified resources – known location, quantity and quality – Undiscovered resources – assumed to exist with unknown data – Reserves – identified resource that can be extracted and sold for a price – Other reserves – undiscovered and identified resources that are not classified as reserves Detection Methods • Several methods are used to detect minerals – Aerial photos & satellite images - outcrops – Radiation-measuring equipment – detect deposits – Magnetometer – record changes in the Earth’s magnetic field – Gravimeter – measures differences in gravity due to density differences in various ore deposits – Underground methods – deep well drilling & core samples – Seismic surveys – analyzing shock waves by detonation – Chemical analysis – leaching into water & plants Mining • Surface mining – equipment strips away the surrounding and unwanted material called the overburden (as waste it is called “spoil”) – – – – – open-pit mining – equipment digs a hole & extracts ore Dredging – draglines scrape up underwater minerals Area strip mining – terrain flattened prior to digging Contour mining – cuts terraces into the terrain Mountain-top removal – explosives & powerful shovels expose ore • Sub-surface mining – deep vertical shafts, explosives, heavy equipment used for extraction Environmental Impacts of Mining • • • • • Scarring & disruption of terrain Collapse of land above mines Toxin laced mining waste & air pollution Acid mine drainage Overall effects on the health of humans and wildlife can be devastating Mineral Supply • Economic depletion – cost is more to find and process than its worth on the open market – – – – – Recycle or reuse Waste less Use less Find a substitute Do without • Depletion time = depletion /time • “Should we continue to mine?” General Mining Law of 1872 • $500 payment & $100/20acres • Management of timber & minerals – Opens land for mineral development – Sell off mineral rich public land – Turn management over to state & local governments Mining Lower Grade Materials • Achieved with current technologies • Can be limited by – Increase cost of mining large quantities of ore – Availability of fresh water – Environmental impact of increased waste & pollution – Environmental impact of disrupting the ecosystem surrounding the mine Microbes in Mining • Bio-mining or in-situ mining is done by inoculating an ore vein with microbes that act on a specific ore • Microbe loosens the ore and provides a means to extract it by flooding the mine • Flood water is filtered for the desired ore and recycled back to the mine • Ex. Copper ore is digested by thiobaccillus ferroxidans • Bio-mining is a slow process Natural Hazards • An ecosystem can be disrupted by natural hazards – – – – – Volcanic eruption Hurricanes Tornadoes Earthquakes Floods • Do the Natural Hazards Lab • Prepare a poster or Power Point presentation that compares & contrasts 2 natural hazards Soil Resources • Complex mixture of – – – – – – Eroded rock Mineral nutrients Decayed organic matter Water Air Organisms (decomposers) • Renewable resource Mature Soil – Soil Zones • Soil Profile – cross section view of the horizontal zones in the soil O * Surface covered with leaves – A * Top soil is composed of a porous mixture of decomposed matter and minerals – B * Sub-soil composed of rocks and other inorganic matter – C * Parent mineral which lies above the bedrock Soil Types • Infiltration – water percolates (seeps) into the zones of soil • Leaching – water picks up minerals as it infiltrates and carries them to lower zones • Soil types in different locations – – – – – Desert Grassland Tropical rainforest Deciduous forest Coniferous forest Soil Permeability & Porosity • Soil permeability – the rate at which water infiltrates the soil • Soil porosity - # of pores/volume of soil – Loams is best for growing crops & contain equal parts of • • • • Clay – holds water Sand – drains easily Salt - minerals Humus – organic matter Soil pH and Nutrient Concentration • Acidity (acidic) – pH is between 1-6.5 – If too acidic, neutralize with lime & fertilize • Neutral – pH is around 7 • Alkalinity (basic) – pH is between 7.5 – 14 – If too basic, add sulfur • Perform the soil lab Soil Erosion • • • • • Movement of soil from place to place Loss of fertile land Build up of soils on land and in water Erosion is occurring faster than soil can form Globally -15% erosion total and 40% of the agricultural property has eroded • US - 1/3 of the prime soil in the US has eroded – USDA states the soil is eroding 16x faster than it forms – USDA states conservation efforts are working Desertification • Desertification is the process of turning fertile land into desert – Drought – long periods without precipitation – Unsustainable human activity – lack of conservation efforts and respect for our land • • • • • • Overgrazing Deforestation Surface mining Erosion Salination Soil compaction Salination • Salination occurs with a concentration of salts in the soil – Irrigation containing salts in the water – Evaporation and transpiration processes leave salts behind – Salts build up to a critical level Waterlogging • Waterlogging occurs when there is too much water remaining on land – Precipitation & irrigation percolates downward – Water table (underground water levels) rise Little Sodus Bay (LSB) Drumlin on LSB– Lake Ontario Drumlin Erosion East of LSB Soil Conservation • 1985 Farm Act – strategy to reduce soil erosion in the US • Reduce erosion & restore fertile land – – – – – – – Conservation tilling – disturb soil as little as possible Terracing – reduce erosion on slopes Contour farming – plant along contours of gentle slopes Strip cropping – planting alternate strips of crops Alley cropping – planting between shrubs and trees Wind breaks Gully reclamation – fast growing vines and shrubs Restoring Soils • Organic material – Animal – dung, adds nitrogen to the soil and stimulates bacterial & fungial action – Green manure – green vegetation tilled into the soil – Compost – rich organic matter produced by bacteria from decomposed organic matter in the presence of oxygen Important Nutrients • Commercial fertilizers contain: – Nitrogen (N) – important for protein production in plants – Potassium (K) - potash – primary agricultural nutrient for food crops – Phosphorous (P) – phosphates - essential nutrient from rocks Soil Lab