* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside the Earth
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
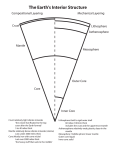
Layers of the Earth What Are The Earth’s Layers ? • • • • Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Characteristics of The Inner Core •Solid ball due to high pressure (most dense layer) •1540 miles across •3700°C = VERY HOT! •Iron and nickel •Intense pressure keeps it from liquefying Characteristic of The Outer Core •Dense liquid molten rock •1400 miles thick •Mainly iron and nickel •Some silicon •Between mantle and inner core •Gives Earth its magnetic field Characteristics of The Mantle • Parts are semimolten (silly putty) • 1800 miles thick • Mantle rock is more dense than crustal rock • Flows in sluggish currents • Between crust and outer core The Crust • Earth’s outer rocky surface • 4 miles thick under oceans • Up to 40 miles thick under mountain ranges • Consists of mostly “light” rocks (granite – below continents) (basalt – below oceans) • Oceans cover 71% of the crust (oceanic crust is very dense) • Continental crust is less dense Oceanic and Continental Crust Note: the directions of movement Tectonic Plates • Earth’s crust is broken into about 19 pieces • These plates move on top of the asthenosphere Earth’s Layers • Are Earth’s layers similar to a hard boiled egg? How Are Earth’s Layers Similar To a Hard Boiled Egg? The Yolk =core , inner & outer core • Egg white • =mantle The Shell =crust Other Physical Structures of the Earth’s Layers • Lithosphere- includes the crust and the upper most portion of the asthenosphere. This area glides over the rest of the upper mantle. Zone of earthquakes/volcanoes. • Asthenosphere- top layer of the upper mantle which consists of highly viscous rock that flows slowly (like hot asphalt)