* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download food web.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
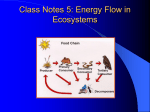
Food Chains, Food Webs, and the Transfer of Energy Autotrophs • A groups of organisms that can use sunlight or chemicals to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose. • In other words, autotrophs are organisms that can make their own food. • Autotrophs are also called producers because they produce all of the food that other organisms use. • Without autotrophs, life on Earth would have become extinct by now. • Most autotrophs are photosynthetic. • Ex. Plants and Algae Photosynthetic Autotrophs Chemosynthetic Autotrophs • Some autotrophs use chemicals available in their environment to make glucose: • These are called Chemotrophs – Chemotrophs get their energy from chemical substances, like hydrogen sulfide. – They live deep in the ocean where there is no sunlight – Ex. Bacteria and some deep-sea worms Heterotrophs • Organisms that DO NOT make their own food. • Another term for Heterotrophs is consumers because they have to consume other organisms in order to live. • There are several kinds of autotrophs, based on what they eat. • Ex. Rabbits, Deer, Mushrooms Heterotrophs Heterotrophs • Herbivores Eat ONLY plants. • Ex. – Cows, Elephants, Giraffes Heterotrophs • Carnivores Eat ONLY meat • Ex. – Lions, Tigers, Sharks Heterotrophs • Omnivores Eat BOTH plants and animals • Ex. – Bears and Humans Heterotrophs • Scavengers and Detritivores feed on the tissue of dead organisms (both plans and animals) • Ex. – Vultures, worms, and pill bugs. Heterotrophs • Decomposers Break down organic molecules and turn them into simple nutrients or fertilizers • Ex. – Bacteria and Mushrooms Food Chains Whenever an organism is consumed by another, energy is transferred into the consumer. • A simple sequence of this type of energy transfer is know as a food chain. • A food chain is simple and direct. • It involves one organism at each trophic level Food Web • Most organisms eat more than JUST one other kind of organism. • When more organisms are involved, we really have several interconnected food chains. • These more complex interconnections are called a food web. Food Web Food Web Notice that the arrows points in the direction of the flow of energy. Trophic Levels • Energy moves from one organisms to another when it is eaten • Each step in this transfer of energy is know as a trophic level Flow of Energy • When a zebra eats grass, it does not get all of the energy that the grass had (much of it is not digested). • When a lion eats a zebra, it does not get all of the energy from the zebra. • No organism EVER receives all of the energy from the organism they just ate • On average, only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next – this is called “the 10% law”. Ecological Pyramid • An ecological pyramid (also called an energy pyramid) shows the relationship between consumers and producers at different trophic levels in an ecosystem. • Shows the relative amounts of energy or matter (biomass) contained at each trophic level. • Shows which level has the most energy and the highest number of organisms. Ecological Pyramid Ecological Pyramid