* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CNS infection
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Social history of viruses wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
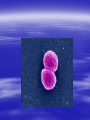
CNS INFECTION Prepare by :Abeer AL-sayeg CNS infection CNS including brain and spinal cord The infection of CNS by both bacteria and virus The infection is fatal and may be cause mortality if not treated in early stage of infection Neisseria menigitidis meningitis Neisseria menigitidis is gram negative diplococcus that may be found with in polymorphonuclear leukocyte about 20% of the population carry this bacteria in the oropharynx It is fatal and relatively high risk period for any individual Symptoms Petechial Septicaemia Endotoxin shook Intracerebral bleeding Diagnoses Blood stained CSF sample Virulence Factors capsule (anti- phagocytic) Lipo-oligosaccharide(LOS) Endotoxine IGA protease Diagnostic Factors Diplococci in spinal fluid (gram stain) Gram negative coffe-bean shaped diplococci Growth on thayer martin media Oxidase positive transmitted colonizes mucosal surfaces of N. meningitidis nasopharynx and is transmitted through direct contact with large droplet respiratory secretions from the patients or asymptomatic carriers. Humans are the only host Treatment Penicillin or third-generation cephalosporin that may be combined with chloramphenicol grouping of meningococci is based on antigenic structure of its capsule . There avaccin protect against gp A and C but not effect against gp B . Heamophilus influenzae b maningitiis Encapsulated strain of plemorphic gram negative pathogenes Respiratory tract May be spread via blood stream from respiratory tract to the brain Nerological damge preventation Infant from 3-4 months are protect from infection by their inhierited maternal antibodies and by age of 3-4 years children will have their own anti-bodies . Vaccing has been develop to protect infant it is given at 2-3 and 4 months age (with other vaccine) Treatment Ampicillin if isolated not produce b-lactmase -athired generation cephalosporin or chloramphenicol. -close contact of children with haemophilus mengitis should receive rifampicin to prevent secondary occuringn. Virus infection Rabies: Old name of Rabies is hydrophobia. Rabies is an invariably fatal infection of human acquired from the bite of an infected mammal Virus infection Rabies is a disease caused by a virus that can affected of CNS of any kind of mammal, including humans . Animals that are infected with rabies can spread the disease through their saliva or brain matter. People may be exposed to rabies when bitten by an infected wild or domestic animal. for rabies is 4 to incubation period The typical 6 weeks. During the incubation period, there .are usually no symptoms of rabies Early symptoms include pain and numbness at the site of the bite symptoms Sore throat . Fever. Headache. Muscle spasm . Convulsion . In ability of patients with rabies to swallow dye to damage to the nerves that control swallowing . symptoms Later symptoms are more distinctive and may include Anxiety Hallucinations Delirium paralysis diagnosed .Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) test:this common, rapid test detects the rabies virus protein. DFA testing is done by taking a sample of tissue from the potentially .affected area diagnosed .Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay This test detects the genetic material (DNA) of the rabies virus proteins. PCR testing is ,very accurate and can be done on saliva .or tissue ,cerebrospinal fluid treated Once rabies symptoms appear, the disease progresses rapidly, and there is no cure. If medical treatment is provided before symptoms develop, the virus almost always is eliminated before it can cause serious damage. Medical treatment for rabies includes: treated Wound care If you are bitten by an animal, clean the wound immediately with plenty of soap and .water to reduce the risk of infection treated vaccinations known as postexposure prophylaxis (PEP). The vaccinations help the body's immune system destroy the disease in its early stages. When the vaccinations are given before more serious symptoms appear, they usually prevent infection from developing THANK YOU