* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Yeast - iGEM 2007
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
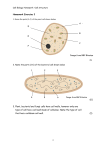
Yeast & Cloning Sergio Peisajovich Lim Lab June 2007 Why Yeast? Experimental Lab The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (also called “baker’s yeast”) is probably the ideal eukaryotic microorganism for biological studies. Yeast genome: fully sequenced and easy to manipulate. Basic mechanisms of yeast cell biology (such as DNA replication, recombination, cell division and metabolism) are highly similar to that of higher organisms (including humans). Yeast Life Cycle Experimental Lab Yeast: Ideal Platform for Synthetic Biology Experimental Lab Add parts, devices or even modules (in an ТextragenomicУ format -plasmid -based- or Тinte gratingУ them within the yeast genome. Delete specific yeast genes, to r emove Тbackground У or interference. Add Тreporter genesУto monitor in real time the function of the synthetic parts/devices/modul es unde r study. Life cycle fa st enough so that we could do all these genetic manipul ations in a reasonable amount of time. Yeast: Adding parts… in plasmids Experimental Lab Parts/Devices/Modules are built in bacteria Transform into Yeast Empty initial plasmid Plasmid coding the desired device Yeast: Adding parts… in plasmids growth in selective medium Experimental Lab Yeast: Adding parts… in plasmids growth in selective medium Experimental Lab Yeast: Adding parts… into the genome Homologous recombination allows genomic integration, but we still need to select: Experimental Lab Yeast: Adding parts… into the genome Part/Device/Module plasmid Experimental Lab Part/Device/Module plasmid URA3 Digest with specific restriction enzyme Linear DNA, ready for yeast transformation and integration Part/Device/Module Incoming Linear DNA Homologous Recombination URA3* Yeast Chromosome Integration (Note that 2 copies, one defective and one functional, of the marker are generated) URA3* Part/Device/Module Yeast Chromosome URA3 Yeast: Adding parts… into the genome Experimental Lab PCR product URA3 plasmid URA3 Linear DNA, ready for yeast transformation and integration URA3 Integration (yfg is now disrupted) yfg URA3 Homologous Recombination Yeast Chromosome Yeast Chromosome Experimental Lab Combinatorial Cloning Part 1 Part 1 Part 2 plasmid plasmid Part 1 Part 2 plasmid plasmid plasmid plasmid Part 3 Experimental Lab Combinatorial Cloning A B B C A D C D Based on Type IIs restriction enzymes A D Experimental Lab Combinatorial Cloning A B B C A D C D Combinatorial Libraries A D A D Experimental Lab Synthetic Biology as Engineering Engineering Negative Feedback Loops Prom Negative Effectors to be used: OspF (MAPK Phosphothreonine Lyase) YopJ (MAPKK Ser/Thr acetylase) YopH (MAPK Tyr phosphatase) Promoters to be used: Constitutive expression (Adhp, CycIp, Ste5p) Inducible by pathway activation (STLp, Fig1p) Protein-interaction domains: Leucine Zippers (high and medium affinities, some with degradation motif) Tag Effector Zipper Term Synthetic Biology as Engineering Engineering Negative Feedback Loops Experimental Lab 1- Combinatorial Cloning in Bacteria 2- Transfer Constructs into Yeast 3- Analyze Pathway Behavior Synthetic Biology as Engineering Engineering Negative Feedback Loops Experimental Lab 1- Combinatorial Cloning in Bacteria DONORS ACCEPTORS Experimental Lab Synthetic Biology as Engineering Engineering Negative Feedback Loops 1- Combinatorial Cloning in Bacteria Prom Tag Effector Zipper Term Synthetic Biology as Engineering Engineering Negative Feedback Loops 2- Transfer Constructs into Yeast 3- Analyze Pathway Behavior FACS Microscopy Experimental Lab