* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbohydrates
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
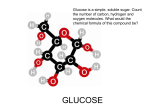
CH2OH H O H OH H H OH HO H OH Carbohydrates: Energy molecules Biology I Carbohydrates Building block molecules = sugars sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar - sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar sugar Carbohydrates Function: quick energy energy storage structure glucose C6H12O6 cell wall in plants sucrose Examples sugars starches cellulose (cell wall) starch How are complex carbohydrates formed and broken down? Dehydration Synthesis Hydrolysis Dehydration Synthesis building bigger molecules from smaller molecules A water molecule is lost building cells & bodies repair growth reproduction + ATP Dehydration Synthesis Dehydration Synthesis Hydrolysis/Digestion taking big molecules apart Hydrolysis splits molecules using water getting raw materials for synthesis & growth making energy (ATP) for synthesis, growth & everyday functions + ATP Example of hydrolysis/digestion ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP starch ATP glucose ATP Starch is digested to glucose Hydrolysis Monosaccharides = Monomers Names for sugars usually end in glucose Fructose galactose -ose CH2OH H O H OH H H OH HO H OH glucose C6H12O6 fructose Disaccharides= Double sugar Made by joining two monosaccharides Lactose (milk sugar) Sucrose (table sugar) Maltose (grain sugar) Building carbohydrates Dehydration Synthesis 1 sugar = monosaccharide | glucose | glucose mono = one saccharide = sugar di = two 2 sugars = disaccharide | maltose Building carbohydrates Dehydration Synthesis 1 sugar = monosaccharide | glucose | fructose How sweet it is! 2 sugars = disaccharide | sucrose (table sugar) Polysaccharides BiG Carbohydrates starch energy storage in plants potatoes glycogen energy storage in animals in liver & muscles cellulose structure in plants poly = many cell walls chitin structure in arthropods & fungi exoskeleton Building BIG carbohydrates glucose + glucose + glucose… = polysaccharide starch (plant) energy storage glycogen (animal) Digesting starch vs. cellulose starch easy to digest cellulose hard to digest enzyme enzyme Cellulose Cell walls in plants herbivores can digest cellulose well most carnivores cannot digest cellulose that’s why they eat meat to get their energy & nutrients cellulose = roughage stays undigested keeps material moving in your intestines Helpful bacteria How can cows digest cellulose so well? BACTERIA live in their stomachs & help digest cellulose-rich (grass) meals Eeeew… Chewing cud? Activities building starch by bonding together paper glucose molecules eat carrots, celery, cookies