O - WordPress.com
... Carbohydrates Most abundant Their abundance in human body is low but constitute about 75% by mass of dry plant materials Green (chlorophyll-containing) plants produce carbohydrates via photosynthesis A major source of energy from our diet composed of the elements C, H and O. They also calle ...
... Carbohydrates Most abundant Their abundance in human body is low but constitute about 75% by mass of dry plant materials Green (chlorophyll-containing) plants produce carbohydrates via photosynthesis A major source of energy from our diet composed of the elements C, H and O. They also calle ...
22A - chemistry
... -1,6-glycosidic bonds (branches occur every 8 to 12 residues - more compact than starch) the total amount of glycogen in the body of a well-nourished adult human is about 350 g, divided almost equally between liver and ...
... -1,6-glycosidic bonds (branches occur every 8 to 12 residues - more compact than starch) the total amount of glycogen in the body of a well-nourished adult human is about 350 g, divided almost equally between liver and ...
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... clear who actually invented it, and references to this particular one appeared in the chemical education literature before publication of the Fiesers’ text. The mnemonic has two features: (1) a system for setting down all the stereoisomeric D-aldohexoses in a logical order; and (2) a way to assign t ...
... clear who actually invented it, and references to this particular one appeared in the chemical education literature before publication of the Fiesers’ text. The mnemonic has two features: (1) a system for setting down all the stereoisomeric D-aldohexoses in a logical order; and (2) a way to assign t ...
Inulin: Non-Starchy Carbohydrate (Fiber).
... Disaccharides are the simplest chains of sugars, made up of two simple sugars linked together. For example, sucrose (table sugar), which is one molecule each of glucose and fructose. Most disaccharides are digestible in the human gut, but some, such as lactose (glucose and galactose linked together) ...
... Disaccharides are the simplest chains of sugars, made up of two simple sugars linked together. For example, sucrose (table sugar), which is one molecule each of glucose and fructose. Most disaccharides are digestible in the human gut, but some, such as lactose (glucose and galactose linked together) ...
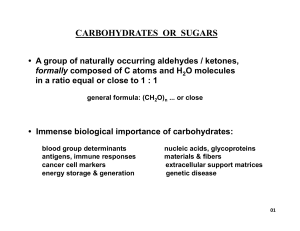
CARBOHYDRATES OR SUGARS
... equilibra7on of the anomers. At equilibrium, the solu7on contains a mixture of ca. 64% of β-‐anomer (all equatorial, more stable) and ca. 36% of α-‐anomer: ...
... equilibra7on of the anomers. At equilibrium, the solu7on contains a mixture of ca. 64% of β-‐anomer (all equatorial, more stable) and ca. 36% of α-‐anomer: ...
1. What are the different kinds of carbohydrates? Be able to define
... What are the structures of monosaccharides, and how are they represented in written formulas? Be able to explain relationships among open-chain and cyclic monosaccharide structures, describe the isomers of monosaccharides, and show how they are represented by Fischer projections and cyclic structura ...
... What are the structures of monosaccharides, and how are they represented in written formulas? Be able to explain relationships among open-chain and cyclic monosaccharide structures, describe the isomers of monosaccharides, and show how they are represented by Fischer projections and cyclic structura ...
الشريحة 1
... The three most abundant hexoses in the biological world are Dglucose, D-galactose, and D-fructose. The first two are Daldohexoses; the third is a D-2-ketohexose. Glucose, by far the most common hexose, is also known as dextrose because it is dextrorotatory. Other names for this monosaccharide are g ...
... The three most abundant hexoses in the biological world are Dglucose, D-galactose, and D-fructose. The first two are Daldohexoses; the third is a D-2-ketohexose. Glucose, by far the most common hexose, is also known as dextrose because it is dextrorotatory. Other names for this monosaccharide are g ...
Carbohydrates
... Cn (H2O)m. Following are two examples of carbohydrates with molecular formulas that can be written alternatively as hydrates of carbon. Glucose (blood sugar): C6H12O6, or alternatively C6 (H2O)6 Sucrose (table sugar): C12H22O11, or alternatively C12 (H2O)11 Not all carbohydrates, however, have this ...
... Cn (H2O)m. Following are two examples of carbohydrates with molecular formulas that can be written alternatively as hydrates of carbon. Glucose (blood sugar): C6H12O6, or alternatively C6 (H2O)6 Sucrose (table sugar): C12H22O11, or alternatively C12 (H2O)11 Not all carbohydrates, however, have this ...
pdf notes
... In 1939 American Chemical Society formed a committee and laid the foundations of modern systematic nomenclature for carbohydrates and derivatives: numbering of the sugar chain, the use of D and L and α and β, and the designation of stereochemistry by italicized prefixes. In 1952, a joint British-Ame ...
... In 1939 American Chemical Society formed a committee and laid the foundations of modern systematic nomenclature for carbohydrates and derivatives: numbering of the sugar chain, the use of D and L and α and β, and the designation of stereochemistry by italicized prefixes. In 1952, a joint British-Ame ...
Chapter 14. CARBOHYDRATES
... Let us consider the following experimental data. If D-glucose is crystallized from aqueous ethanol, the pure αform is obtained. On crystallization of D-glucose from acetic acid, another product was isolated, the β form. Both forms of D-glucose are diastereomers since they differ only in the configur ...
... Let us consider the following experimental data. If D-glucose is crystallized from aqueous ethanol, the pure αform is obtained. On crystallization of D-glucose from acetic acid, another product was isolated, the β form. Both forms of D-glucose are diastereomers since they differ only in the configur ...
Chapter 12 Lecture Notes: Carbohydrates
... characterize the glycosidic linkage by the bonding pattern [for example: β(1⟶4)]. 13. Given the Haworth structures of two monosaccharides, be able to draw the disaccharide that is formed when they are connected by a glycosidic bond. 14. Understand the difference between homopolysaccharides and heter ...
... characterize the glycosidic linkage by the bonding pattern [for example: β(1⟶4)]. 13. Given the Haworth structures of two monosaccharides, be able to draw the disaccharide that is formed when they are connected by a glycosidic bond. 14. Understand the difference between homopolysaccharides and heter ...
Slide 1
... Sucrose g Glucose + Fructose (Sucrase = brush border disaccharidase) Lactose g Glucose + Galactose (Lactase = brush border disaccharidase) Isomaltase g the only enzyme that digests a-1,6 glycosidic bonds. ...
... Sucrose g Glucose + Fructose (Sucrase = brush border disaccharidase) Lactose g Glucose + Galactose (Lactase = brush border disaccharidase) Isomaltase g the only enzyme that digests a-1,6 glycosidic bonds. ...
Chapter 4
... The Simple Carbohydrates • Disaccharides are pairs of monosaccharides, one of which is always glucose Condensation reactions link monosaccharides together. Hydrolysis reactions split molecules and commonly occur during digestion. Maltose consists of two glucose units. It is produced during th ...
... The Simple Carbohydrates • Disaccharides are pairs of monosaccharides, one of which is always glucose Condensation reactions link monosaccharides together. Hydrolysis reactions split molecules and commonly occur during digestion. Maltose consists of two glucose units. It is produced during th ...
0ac97eb570ee16e
... The Simple Carbohydrates • Disaccharides are pairs of monosaccharides, one of which is always glucose Condensation reactions link monosaccharides together. Hydrolysis reactions split molecules and commonly occur during digestion. Maltose consists of two glucose units. It is produced during th ...
... The Simple Carbohydrates • Disaccharides are pairs of monosaccharides, one of which is always glucose Condensation reactions link monosaccharides together. Hydrolysis reactions split molecules and commonly occur during digestion. Maltose consists of two glucose units. It is produced during th ...
Carbohydrates - Carone Fitness
... grain because they provide the most vitamins and minerals and are often rich in fiber. Refined grains such as white flour and white rice are considered “processed” foods that are generally stripped of their nutrients and fiber. In general, it is recommended that the bulk of one’s diet come from whol ...
... grain because they provide the most vitamins and minerals and are often rich in fiber. Refined grains such as white flour and white rice are considered “processed” foods that are generally stripped of their nutrients and fiber. In general, it is recommended that the bulk of one’s diet come from whol ...
Carbohydrate Chemistry - National Open University of Nigeria
... of these gave all the characteristic reactions of glucose, and when dissolved in water equilibrated to the same mixture. This equilibration takes place over a period of many minutes, and the change in optical activity that occurs is called mutarotation. These facts are summarized in the diagram belo ...
... of these gave all the characteristic reactions of glucose, and when dissolved in water equilibrated to the same mixture. This equilibration takes place over a period of many minutes, and the change in optical activity that occurs is called mutarotation. These facts are summarized in the diagram belo ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... fructose portion of sucrose has a hemiacetal or hemiketal group, thus the two hexoses must have a glycoside linkage that involves C-1of glucose and C-2 of fructose. 4. The hydrolysis of sucrose indicates an α configuration at the glucoside portion and an enzyme known to hydrolyze a ...
... fructose portion of sucrose has a hemiacetal or hemiketal group, thus the two hexoses must have a glycoside linkage that involves C-1of glucose and C-2 of fructose. 4. The hydrolysis of sucrose indicates an α configuration at the glucoside portion and an enzyme known to hydrolyze a ...
CARBOHYDRATES
... arbohydrates are a major class of naturally occurring organic compounds, which come by their name because they usually have, or approximate, the general formula C,,(H,O),,,, with n equal to or greater than three. Among the well-known carbohydrates are various sugars, starches, and cellulose, all of ...
... arbohydrates are a major class of naturally occurring organic compounds, which come by their name because they usually have, or approximate, the general formula C,,(H,O),,,, with n equal to or greater than three. Among the well-known carbohydrates are various sugars, starches, and cellulose, all of ...
MCAT Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 22: Carbohydrates
... There are 6 carbons present so it is a hexose. Check the anomeric carbon. If there is a hemiacetal present, then the carbohydrate is an aldose. If there is a acetal present, then the carbohydrate is a ketose. Here, a hemiacetal is present so it is an aldose. The statement is correct. (C) states the ...
... There are 6 carbons present so it is a hexose. Check the anomeric carbon. If there is a hemiacetal present, then the carbohydrate is an aldose. If there is a acetal present, then the carbohydrate is a ketose. Here, a hemiacetal is present so it is an aldose. The statement is correct. (C) states the ...
Document
... - and anomers freely interconvert @ thermodynamic equilibrium—eg glucose is predominantly a mixture of such anomers with negligible contributions from the linear form ...
... - and anomers freely interconvert @ thermodynamic equilibrium—eg glucose is predominantly a mixture of such anomers with negligible contributions from the linear form ...
Chapter 7 - Chemistry
... - associated with sweetness with most monosaccharides (but not all) and many disaccharides (but not all) having sweet taste - trioses are smallest monosaccharides that can exist: i) one is an aldose (glyceraldehyde) reference cmpds for all ii) one is a ketose (dihydroxyacetone) ketoses and aldoses N ...
... - associated with sweetness with most monosaccharides (but not all) and many disaccharides (but not all) having sweet taste - trioses are smallest monosaccharides that can exist: i) one is an aldose (glyceraldehyde) reference cmpds for all ii) one is a ketose (dihydroxyacetone) ketoses and aldoses N ...
Document
... Hemiacetal is still fairly reactive. So hemiacetal can react with an alcohol and produce an acetal. o You know it is an acetal because you see a carbon with two oxygens linked to it, both with some other substituent. Slide 40 Sugar acetals are called glycosides: You can get sugars to form acetal ...
... Hemiacetal is still fairly reactive. So hemiacetal can react with an alcohol and produce an acetal. o You know it is an acetal because you see a carbon with two oxygens linked to it, both with some other substituent. Slide 40 Sugar acetals are called glycosides: You can get sugars to form acetal ...
Derived copy of Bis2A 03.2 Carbohydrates
... from the body: ber binds to the cholesterol in the small intestine, then attaches to the cholesterol and prevents the cholesterol particles from entering the bloodstream, and then cholesterol exits the body via the feces. Fiber-rich diets also have a protective role in reducing the occurrence of co ...
... from the body: ber binds to the cholesterol in the small intestine, then attaches to the cholesterol and prevents the cholesterol particles from entering the bloodstream, and then cholesterol exits the body via the feces. Fiber-rich diets also have a protective role in reducing the occurrence of co ...
Sucrose
Sucrose is a common, naturally occurring carbohydrate found in many plants and plant parts. Saccharose is an obsolete name for sugars in general, especially sucrose. The molecule is a disaccharide combination of the monosaccharides glucose and fructose with the formula C12H22O11.Sucrose is often extracted and refined from either cane or beet sugar for human consumption. Modern industrial sugar refinement processes often involves bleaching and crystallization also, producing a white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste of pure sucrose, devoid of vitamins and minerals. This refined form of sucrose is commonly referred to as table sugar or just sugar. It plays a central role as an additive in food production and food consumption all over the world. About 175 million metric tons of sucrose sugar were produced worldwide in 2013.The word ""sucrose"" was coined in 1857 by the English chemist William Miller from the French sucre (""sugar"") and the generic chemical suffix for sugars -ose. The abbreviated term Suc is often used for sucrose in scientific literature.