* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 38 Plant Nutrition - Tri
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
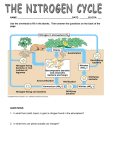
Chapter 37 Plant Nutrition Biology 102 Tri-County Technical College Pendleton, SC Macro versus Micronutrients Macronutrient is nutrient required by plant in large amounts Micronutrient is nutrient required by plant in small amounts Micronutrients: Carbon (CO2)-major component of plant’s organic compounds Oxygen (CO2)-major component of plant’s organic compounds Macronutrients, cont. Hydrogen (H2O)-major component of plant’s organic compounds Nitrogen (NO3-; NH4+)-component of nucleic acids, proteins, hormones, and coenzymes Sulfur (SO42-)-component of proteins & coenzymes Macronutrients, cont. Phosphorous (H2PO4-; HPO42-)-component of nucleic acids, phospholipids, ATP, & several coenzymes Potassium (K+)-cofactor that functions in protein synthesis, major solute functioning in water balance, & operation of stomata Calcium (Ca2+)-formation and stability of cell walls, maintenance of membrane structure and permeability, activates some enzymes, regulates many responses of cells to stimuli Macro and Micro Magnesium (Mg2+)-component of chlorophyll, activates many enzymes MICRONUTRIENTS: Chlorine (Cl-)-required for watersplitting step of photosynthesis, functions in water balance Iron (Fe3+; Fe2+)-component of cytochromes, activates some enzymes Micronutrients, cont. Boron (H2BO3-)-cofactor in chlorophyll synthesis, may be involved in carbohydrate transport and nucleic acid synthesis Manganese (Mn2+)-active in formation of amino acids, activates some enzymes, required for water-splitting step of photosynthesis Zinc (Zn2+)-active in formation of chlorophyll and activates some enzymes Micronutrients, cont. Copper (Cu+; Cu2+)-component of many redox and lignin-biosynthetic enzymes Molybdenum (MoO42-)-essential in nitrogen fixation and cofactor that functions in nitrate reduction Nickel (Ni2+)-cofactor for enzyme functioning in nitrogen metabolism Micronutrient Why’s? Most micronutrients function as cofactors of enzymatic reactions Because micronutrients generally play catalytic roles that plants need only minute quantities of these elements Example: only 1 molybdenum atom for each 16 million atoms of hydrogen in dried plant material Plants and Nitrogen Plants require nitrogen to produce proteins, nucleic acids, and other organic molecules They CANNOT use nitrogen in gaseous form (N2) To be used, must be in form of ammonium (NH4+) or nitrate (NO3-) Plants acquire most of their nitrogen in the form of nitrate (NO3-) Plants and Nitrogen, cont. Nitrate produced in soil by nitrifying bacteria They oxidize ammonia/ammonium Other species of nitrogen fixing bacteria live in plant roots (mutualistic symbiotic relationship) Nitrogen absorbed by plant is incorporated into organic compounds Nitrogen Cycle Visual Miracle Grow or thereabouts… Ever purchase a bag of triple 13? No, how about triple 10? 13-13-13 or 10-10-10 Not brain surgery…is by weight so close Lists contents in order of: Nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium N-P-K 21-0-0 (Oh yeah…but….) Nitrogen Fixation Few species of bacteria possess enzyme that will convert nitrogen gas to ammonia (N2 NH3) Essential to life on this planet Cyanobacteria and Rhizobium Rhizobium “infects” roots of plants causing nodulation These nodes are site of bacteria nitrogen fixing Knowing the Nodes Nitrogen Fixation Visual Bits and Pieces… Mutualistic symbiotic relationship Mycorrhizae is mutualistic relationship between fungus and plant roots Increases absorption of water and minerals (especially phosphorus) Can be ECTO or ENDO (This should be a review from Bio 101) Heterotrophic/Carnivorous Plants Some plants have lost ability to sustain themselves by photosynthesis Mistletoes, dodders, and Indian pipe Kind of ify for mistletoe but…. Extract nutrients from hosts by absorptive organs called haustoria Approximately 450 plant species are carnivorious H/C Plants, cont. Do not live by photosynthesis alone Venus fly trap, sundews, & pitcher plants Most live in acidic environments Difficult for decay-causing organisms to break down bodies of dead organisms Hence, not much recycling These plants evolved way to supply their nitrogen (and phosphorous) needs by “eating protein”