* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
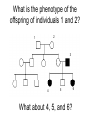
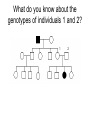
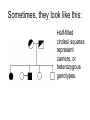
DNA is very important Or How it can change the world Pedigree symbols What is the phenotype of the offspring of individuals 1 and 2? 2 1 3 4 5 What about 4, 5, and 6? 6 What do you know about the genotypes of individuals 1 and 2? 1 2 Sometimes, they look like this: Half-filled circles/ squares represent carriers, or heterozygous genotypes. Karytopye – picture of all chromosomes Shows chromosome abnormalities Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome Klinefelter Syndrome Cri-Du-Chat Jacobs Syndrome Mutations: the good, the bad, and the indifferent • Point mutations • Frame-shift mutations • Not all mutations are bad – some make bacteria ANTI-BIOTIC RESISTANT. Good for the bacteria, not-so-good for you! • Some mutations result in no change Mutations are changes in DNA • Changes in DNA result in changes in the protein. • Changes in the protein can introduce new characteristics (blonde hair) • New traits can be passed to offspring Mutations can change a population • If new traits are advantageous, those individuals will have more offspring with the new traits. • Over long periods of time, these populations can become new species. • Species are defines as groups that can breed with each other and produce VIABLE offspring. This is Natural Selection. New species can develop if… • Members of a populations are separated from each other (GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION) • Members of two populations stop breeding with each other (REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION) • Having an abnormal number of chromosomes (POLYPLOIDY) Divergent Evolution • One ancestral species leads to 2 new species Marine Iguana Land Iguana Ancestral Green Iguana Adaptive Radiation • One ancestral species leads to 3 or more new species Gradualism or Punctuated Equilibrium? • Two ideas of how new species develop Gradualism: lots of small changes in DNA over long periods of time Punctuated Equilibrium: fewer, larger changes over long periods of time. Gradualism 10 million years Punctuated Equilibrium 10 million years Notice the results of both are the same: CHANGE A cladogram is like a family tree showing how things have changed. Shows relationships based on specific characteristics Point where common ancestors diverged Everything to the right of this point have Vertebrae Phylogenetic tree shows relationships between organisms. Each “split” represents a common ancestor A type of Cladogram that shows the relationships between organisms with a common ancestor Living things are grouped according to similarities • • • • • • • Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Largest Smallest Binomial Nomenclature: scientific names are Genus and Species Ex. Iguana iguana Living things are grouped according to similarities • Homologous structures (homo=same) VS Analogous structures (not the same, but same function) - bird wings and bat wings -bird wings and insect wings Living things are grouped according to similarities • Embryology Organisms that have similar embryonic development are more closely related Dichotomous keys • Species can be identified using a dichotomous key • Series of “either / or” questions leading to the identification. Dichotomous keys Example: 1. Does the flower have white or yellow petals? -if yellow, it is a sunflower -if white, go to question 2 2. Does the flower have a yellow or red center? -if yellow, it is a daisy -if red, go to question 3