* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Food Web power point
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
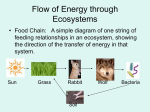
Food Webs and Energy Pyramids Objectives • Identification of the feeding relationships of animals in an ecosystem • Tracing the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem • Understanding how organisms in an ecosystem are interrelated • Understanding the complex and dynamic nature of an ecosystem. Ecosystems • Biotic Factors: Any living part of an environment. • Abiotic Factors: Any non-living part of an environment. Examples: Feeding Strategies • Autotroph - organisms that is able to capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds, also called a producer. • Heterotroph -organisms that obtain food by consuming other living things, also called a consumer. Feeding Strategies • Producers/Autotroph- Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. – Definition-organisms that can capture energy from sunlight and use that energy to produce food. – Examples: Feeding Strategies • Consumers/Heterotrophs • Definition:-organisms that rely on other organisms for their energy and food. • Examples: – Herbivores- such as cows, obtain energy by eating only plants. – Carnivores- such as snakes, eat only animals. – Omnivores- such as humans, eat both plants and animals. – Detritivores- such as earthworms, feed on dead matter. – Decomposers- such as fungus, break down organic matter. – Scavengers- such as vultures, consume the carcass of other animals. Trophic Levels Energy, Producers, and Consumers Trophic Levels • Producers • Definition- the beginning level in a food chain that contains organisms that use energy directly from the sun for life processes. For example: Plants and other autotrophs use sunlight to produce sugars and oxygen. • Examples: plants, some protists (algae), some bacteria (cyanobacteria) Trophic Levels • Primary Consumers • Definition- Organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming producers. They indirectly use energy from the sun that was captured by the producers. For example: when plants are eaten by animals. • Examples: Rabbits, field mice, birds, and prairie dogs. Trophic Levels • Secondary Consumers • Definition- Organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming other consumers. They indirectly use energy from the sun that was captured by the producers and other consumers. • For example: Foxes, birds, snakes Trophic Levels • Tertiary Consumers and Top Predator Definition: Tertiary Consumers are carnivores /organisms that eat only animals and they feed on secondary and primary consumers. Examples: Harris’s Hawks, rattlesnakes, dogs, owls, bald eagles, plankton-eating fish, shrew, lions and tigers. Trophic Levels • Detritivores – Definition – organisms that consume dead and decaying organic matter http://www.bing.com/images Trophic Levels • Decomposers Definition: Organisms that break down and obtain energy from dead organic matter. Examples: Bacteria, fungi, mushrooms, mites, gitterbug, millipede, slug, earthworm, snail, and the dung beetle. Trophic Levels Trophic Levels Food Chain vs. Food Web A food chain is a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. Food Chain vs Food Web A food web is a network of several interacting food chains. Dynamic Nature of Ecosystems Changes in Ecosystem • Top Down – Owls increase – Mice decline – Grass increases Changes in Ecosystem • Bottom up – Add fertilizer- more grass – More mice – More owls Energy Pyramid Energy transfer is only 10% from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level Lots of produces Few top predators