* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internal Factors to Consider in Pricing
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Transfer pricing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
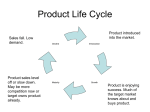
Pricing After today’s class you should understand: • The factors to consider in pricing • How pricing relates to other parts of the marketing mix • How pricing strategies vary across the product lifecycle. Internal Factors to Consider in Pricing • Marketing Objectives – – – – Survival (Penetration) Current Profit Maximization (Skimming) Market Share Leadership (Penetration) Product Quality Leadership (Skimming) • Costs – Caapcity (Don’t vary with production) » overhead – Variable (Vary directly with every unit produced) » Materials – Expenses (Controllable and Vary depending on the sales goals for the period.) » Promotional/Selling Costs The Learning Curve and Pricing • As people do the same thing over and over they do it faster and with less mistakes. This is known as the learning curve. • Companies which make a lot of a product tend to have variable cost advantages. • In addition, companies which make a lot of a product have low fixed costs per unit. • Thus, they can price lower and still make the same gross margin as another company. This can be a strategic competitive advantage. The Learning Curve-An Example Company A Units 50,000 Fixed Costs $100,000 Fixed Costs per unit $2.00 Variable costs per unit $1.00 Total Costs per unit $3.00 Company B 100,000 $125,000 $1.25 $.75 $2.00 Price Elasticity of Demand % change in quantity demanded % change in price • The more elastic the demand the more it pays for the seller to lower the price. Quick Think: What are the Factors influencing Price Elasticity Drivers of the factors influencing price elasticity The other elements of the marketing mix. Product Place Promotion Buyer Reaction to Price Changes • Reference prices are prices that customers carry around in their mind when they look at a given product. • Promotional pricing tends to lower reference prices. • Once you’ve lowered the reference price it is very difficult to raise it again. • Ways to successfully raise price – Negotiated pre-agreements – Successful arguments based on cost or inflation increases – Unbundling – Salesforce management Competitor responses to Price Changes • Competitors are most likely to react when – – – – The competitor is large The number of competitors in the market is small When the product is uniform When buyers are well-informed • Competitor interpretations of price cuts – A market share grab – A company in trouble – Company wants the industry as a whole to reduce prices and increase the size of the pie.