* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Distribution Concepts
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
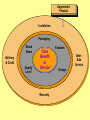
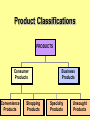
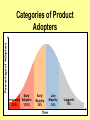
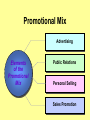
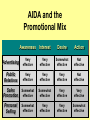
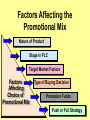
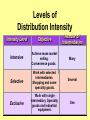
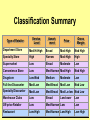
Product, PLC and Services Chapters 10 - 12 What is a Product? • Anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a want or need. It is usually judged on (1) product features (2) services mix & quality and (3) price appropriateness • Core benefit, Basic product, Expected product, Augmented product, Potential product Augmented Product Installation Packaging Brand Name Delivery & Credit Quality Level Core Benefit or Service Warranty Features AfterSale Service Design Product Classifications PRODUCTS Consumer Products Convenience Products Shopping Products Business Products Specialty Products Unsought Products Depth of the product lines Gillette’s Product Lines & Mix Width of the product mix Blades and razors Toiletries Mach 3 Sensor Trac II Atra Swivel Double-Edge Lady Gillette Super Speed Twin Injector Techmatic Series Adorn Toni Right Guard Silkience Soft and Dri Foamy Dry Look Dry Idea Brush Plus Writing instruments Lighters Paper Mate Flair Cricket S.T. Dupont Product Line Strategies • Extensions: Adding additional products to an existing product line in order to compete more broadly in the industry. • Contractions: deleting products from product lines if there are low sales, cannibalization, obsolesce or few resources. The Product Life Cycle Introductory Growth Stage Stage Maturity Stage Decline Stage Product Dollars Category Sales Product Category Profits 0 Time Introduction Stage • • • • • • • High failure rates Little competition Frequent product modification Limited distribution High marketing and production costs Negative profits Promotion focuses on awareness and information • Intensive personal selling to channels Growth Stage • • • • • • • • Increasing rate of sales Entrance of competitors Market consolidation Initial healthy profits Promotion emphasizes brand ads Goal is wider distribution Prices normally fall Development costs are recovered Maturity Stage • • • • • • • • Declining sales growth Saturated markets Extending product line Stylistic product changes Heavy promotions to dealers and consumers Marginal competitors drop out Prices and profits fall Niche marketers emerge Decline Stage • Long-run drop in sales • Large inventories of unsold items • Elimination of all nonessential marketing expenses • Options for Deleting Products: • • • • Maintaining Deletion Harvesting Contracting Marketing Strategies for PLC INTRODUCTION Product Strategy Distribution Strategy Promotion Strategy Pricing Strategy Limited models Frequent changes GROWTH More models Frequent changes. Limited Expanded Wholesale/ dealers. Longretail distributors term relations MATURITY DECLINE Large number Eliminate of models. unprofitable models Extensive. Margins drop. Shelf space Awareness. Aggressive ads. Advertise. Stimulate Stimulate Promote heavily demand.Sampling demand Higher/recoup Fall as result of Prices fall competition & development (usually). efficient produccosts tion. Phase out unprofitable outlets Phase out promotion Prices stabilize at low level. Percentage of Adopters Categories of Product Adopters Early Innovators Adopters 2.5% 13.5% Early Majority 34% Time Late Majority 34% Laggards 16% Diffusion Process and PLC Curve Introduction Growth Decline Maturity Sales Product life cycle curve Early majority Late majority Early adopters Innovators Laggards Diffusion curve Pricing Concepts Chapters 13 Price and Value • Value = perceived benefits/price • Price = perception of quality • Price = consumer perception of prestige • Example: – Swiss firm TAG HEUER – Changed prices from $250 to $1000 – Sales volume increased sevenfold Step 1: Pricing Objectives • Survival • Maximum current profit/profit oriented pricing • Maximum market share/sales oriented pricing • Maximum market skimming • Product quality leadership Step 2: Determining Demand 2.50 S Surplus D Price 2.00 Price Equilibrium 1.50 1.00 Shortage S .50 0 20 40 60 80 Quantity demanded 100 D 120 Elasticity of Demand Consumers sensitivity to price changes Price Goes... Revenue Goes... Demand is... Down Up Elastic Down Down Inelastic Up Up Inelastic Up Down Elastic Up or Down Stays the Same Unitary Elasticity Factors that Affect Elasticity • DEMAND LESS ELASTIC IF: – Few or no substitutes – Buyers don’t notice higher price – Buyers are slow to change habits – Buyers think higher prices are justified Step 3: Estimating Cost • Variable costs – changes with level of output • Fixed costs – no change with output level • Marginal costs – the change in total costs associated with a 1 unit change in output • Average variable costs – total variable costs divided by quantity of output • Average total costs – total costs divided by quantity of output Step 4: Analyzing Competition • Analyze competitors costs, prices and offers Step 5: Methods of Setting Prices • Markup pricing – Target return pricing • Perceived value pricing Step 6: Selecting Final Price • Psychological pricing • Marketing mix • Company policies Promotion Concepts Chapter 16 What is Promotion? Informing Reminding Target Audience Persuading Communication by marketers that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers of a product in order to influence an opinion or elicit a response. Developing Effective Marketing Communications • • • • • • • • Identify the target audience Determine Communication objectives Design the message Select the communication channels Budget Determine the media mix Measure the results Manage the IMC process Promotional Mix Advertising Elements of the Promotional Mix Public Relations Personal Selling Sales Promotion Design the Message: AIDA Concept Action Desire Interest Attention AIDA and the Promotional Mix Awareness Interest Desire Action Advertising Very effective Very effective Somewhat effective Not effective Public Relations Very effective Very effective Very effective Not effective Sales Promotion Somewhat effective Somewhat effective Very effective Very effective Personal Selling Somewhat effective Very effective Very effective Somewhat effective Designing the Message • Message content – Rational appeals, moral appeals, emotional appeals • Message structure – One sided vs. two sided messages • Message format • Message source – Source credibility Select Communication Channels • Personal communication channels • Nonpersonal communication channels (which is what we will focus on for this class) Establishing the Budget • • • • Affordable method Percentage of sales method Competitive parity method Objective and task method Factors Affecting the Promotional Mix Nature of Product Stage in PLC Target Market Factors Factors Affecting Choice of Promotional Mix Type of Buying Decision Promotion Funds Push or Pull Strategy Sales ($) Product Life Cycle and the Promotional Mix Maturity Introduction Growth Decline Time Light Heavy use of Advertising, advertising, prePR for introduction awareness; Publicity sales promotion for trial Advertising, PR, Brand loyalty Personal Selling for distribution Ads decrease. Sales Promotion, Personal Selling Reminder & Persuasive AD/PR decrease Limited Sales Promotion, Personal Selling for distribution Push and Pull Strategies PUSH STRATEGY Manufacturer promotes to wholesaler Wholesaler promotes to retailer Retailer promotes to consumer Consumer buys from retailer Orders to manufacturer PULL STRATEGY Manufacturer promotes to consumer Consumer demands product from retailer Retailer demands product from wholesaler Orders to manufacturer Wholesaler demands product from manufacturer Distribution Concepts Chapter 14 - 15 Value Networks & Marketing Channels • Value network: partnerships that a firm creates to source, augment and deliver its offerings. • Marketing Channel: A set of interdependent organizations that ease the transfer of ownership as products move from producer to business user or consumer. • Functions of Channels: – Specialization of labor – Overcoming discrepancies & gaps – Providing contact efficiency Channel Structure for Consumer Products Direct Channel Producer Retailer Channel Producer Wholesaler Agent/Broker Channel Channel Producer Producer Agents or Brokers Consumers Wholesalers Wholesalers Retailers Retailers Retailers Consumers Consumers Consumers Alternative Arrangements • Multiple channels – two+ channels to distribute the same product • Nontraditional channels – infomercials, mail order, internet etc. • Strategic channel alliances – use another manufacturer’s already established channel Factors that Affect Channel Choice • Market factors – Customer profiles – Type of customer – Market size and geographic location • Product factors – Product complexity – Price – PLC • Producer factors – Resources – Desire for control Levels of Distribution Intensity Intensity Level Objective Number of Intermediaries Intensive Achieve mass market selling. Convenience goods. Many Selective Work with selected intermediaries. Shopping and some specialty goods. Several Exclusive Work with single intermediary. Specialty goods and industrial equipment. One Managing Channel Relationships – Social Dimensions • Channel power • Channel control • Channel conflict – Horizontal conflict – Vertical conflict • Legal & ethical issues in channel relations Classification Summary Type of Retailer Service Level Assortment Price Gross Margin Department Store Mod Hi-High Broad Mod-High Mod High Specialty Store High Narrow Mod-High High Supermarket Low Broad Moderate Low Convenience Store Low Med-Narrow Mod High Mod High Drugstore Low-Mod Medium Moderate Low Full-line Discounter Mod-Low Med-Broad Mod Low Mod Low Specialty Discounter Mod-Low Med-Broad Mod Lo-low Mod Low Warehouse Clubs Low Broad Low-lower Off-price Retailer Low Med-Narrow Low Low Restaurant Low-High Med-Narrow Low-High Low-High Low Nonstore Retailing Automatic Vending Direct Retailing Major Forms of Nonstore Retailing Direct Marketing Electronic Retailing