* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Transcranial Doppler wikipedia , lookup
Cortical stimulation mapping wikipedia , lookup
Brain damage wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
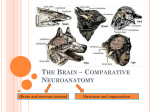
Class Slides Set 16B Brains The brains . . . apes and humans have large heads and brains (relative to body size) Human and Ape Brains Humankind Emerging, 7th ed., p. 389 The brains . . . the large brains of apes and humans are also more developed than those of other animals ... The brains develop in . . . • size . . . • complexity . . . • the ratio of brain weight to overall body weight . . . The brains develop in . . . • size . . . • complexity . . . • the ratio of brain weight to overall body weight . . . Cranial Capacity… Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 9th ed., p. 207 Cranial Capacity… Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 9th ed., p. 207 Cranial Capacity… Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 9th ed., p. 207 The brains develop in . . . • size . . . • complexity . . . • the ratio of brain weight to overall body weight . . . Lateral view of the brain. The illustration shows the increase in the cerebral cortex of the brain. The cerebral cortex integrates sensory information and selects responses. Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 9th ed., p. 107 The brains . . . humans have highly developed frontal and occipital regions of the brain . . . The brains . . . occipital region = curved back and base of the skull Gracile Australopithecus / Homo Lineage Brain Humankind Emerging, 7th ed., p. 390 The brains . . . cerebrum = • large rounded structure of the brain • largest part of the brain • comprises ca. 85% of the brain’s total weight Lateral view of the brain. The illustration shows the increase in the cerebral cortex of the brain. The cerebral cortex integrates sensory information and selects responses. Understanding Physical Anthropology and Archaeology, 9th ed., p. 107 The brains . . . The cerebral cortex (neocortex) increases in area The brains . . . cerebral cortex = neocortex = thin layer of grey matter covering the cerebrum The brains . . . in humans the cerebral cortex lies in folds or “convolutions” over the entire surface of the cerebral hemisphere The brains . . . prehistorically the convoluted cerebral cortex can often be seen in “endocasts” The brains . . . endocasts = fossilized casts of the interior of a skull The brains . . . humans also have well-developed “association” areas . . . The brains . . . association areas are thought to be involved in learning, memory, thinking, and bringing together information form the various senses The brains . . . association areas = regions of the cerebral hemispheres thought to serve some integrative function . . . Human Brain Humankind Emerging, 7th ed., p. 389 The brains develop in . . . • size . . . • complexity . . . • the ratio of brain weight to overall body weight . . . (“brain weight / body weight ratio”) Brain Weight – Body Weight Ratios Humankind Emerging, 7th ed., p. 386 http://www.d.umn.edu/cla/faculty/troufs/anth1602/pcbrain.html Continue on to Set # 16C Next: Teeth / Jaw Diet