* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Autosomal Dominance Inheritance
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
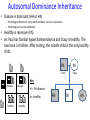
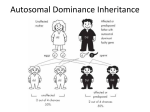
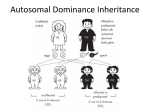
Autosomal Dominance Inheritance What’s an Autosome? • Autosome: Non sex chromosome – Ex: Autosomal disorders: gene for the disease is found on chromosomes 1-22 • Autosomal Recessive Inheritance – Must inherit two copies of the disorder to be affected – Healthy is dominant (HH or Hh) – Disease is recessive (hh) – Ex: Cystic fibrosis, PKU, Albinism, Sickle cell anemia • Autosomal Dominance Inheritance – Only need to inherit one copy of the disorder to be affected – Disease is dominant (HH or Hh) – Healthy is recessive (hh) – Ex: Familial hypercholesterolemia (also called FH), Huntington’s disease, Neurofibromatosis Autosomal Dominance Inheritance • Disease is dominant (HH or Hh) – Homozygous dominant: early death and don’t survive to reproduce – Heterozygous live into adulthood • Healthy is recessive (hh) • ex: Paul has familial hypercholesterolemia and Stacy is healthy. The two have 3 children. After testing, the middle child is the only healthy child. Hh hh Paul Stacy Key disease disease H = FH disease h= healthy healthy healthy Hh hh Hh Autosomal Dominance Inheritance • Huntington’s disease is a dominant disorder found on chromosome 4. Betty and Marcus met at a support clinic they have been attending to help them cope with the knowledge of their illness with Huntington’s disease. They would like to know the risk of having a healthy child, now that Betty is pregnant. Hh Hh Marcus Betty Key Disease (severe) disease H = Huntington’s disease h = healthy disease healthy ? Woody Guthrie: This Land is Made for You and Me Video about Huntington's disease • Autosomal dominant disorder • Brain cells start to die in late 30’s • Causes uncontrollable muscle jerking • Death usually in 40’s-50’s • No treatments Click if YouTube video doesn’t work