* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ex. AA, Aa, aa
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
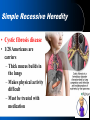
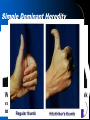
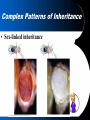
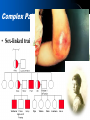
Chapter14: Human Heredity Making a Pedigree • Pedigree – A graphic representation of genetic inheritance. – Track genotypes by looking at their phenotypes – Genotype- allele combination for genes that express a trait (ex. AA, Aa, aa) – Phenotype- physical traits caused by a genotype( ex. AA= red flowers, aa= white flowers Carrier- person who can pass on a disease but it not effected by it Reading a Pedigree • Is this a dominate or recessive disease? • Which individuals MUST be carriers? • I-1,2; II-1 or 2; III3,4 • What are the possible genotypes for III-1? • AA or Aa Recessive (aa) Aa Aa AA or Aa Aa Aa aa Aa Aa aa aa Reading a Pedigree • Is this a dominate or recessive disease? • Which individuals MUST be carriers? aa AA or Aa Dominate (AA, Aa) Aa Aa -None. Cannot have carries for a simple dominate disease • What are the possible genotypes for IV-1? -AA or Aa Aa AA or Aa aa Aa aa Simple Recessive Heredity • Recessive traits can remain dormant and can appear suddenly; carriers • Tend to skip generations • Some recessive disease are fatal and have late onset; disease starts when you are an adult Simple Recessive Heredity • Cystic fibrosis disease • 1/28 Americans are carriers – Thick mucus builds in the lungs – Makes physical activity difficult – Must be treated with medication Simple Recessive Heredity • Phenylketonuria (PKU) – Body lacks enzyme to change phenylalanine to tyrosine – Build up in the body leads to a damaged nervous system – Fetuses are tested to treat with diet Simple Dominant Heredity • Heredity of many physical characteristics – Widow’s peak hairline – Darwin earlobes – Hitchhiker’s thumb • Traits appear in every generation and is equally spread between males and females Complex Patterns of Inheritance • Multiple phenotypes from multiple alleles • Traits controlled by more than two alleles have multiple alleles • Blood Type IA, IB, or I, different combinations make blood types Complex Patterns of Inheritance • Polygenic inheritance – Polygenic inheritance is the inheritance pattern of a trait that is controlled by two or more genes. – Alleles are not dominate or recessive; they represent degrees of expression – All heterozygotes are intermediate in phenotype. Complex Patterns of Inheritance • Sex determination : – chromosomes, which determine the sex of an individual, are called sex chromosomes. – All other chromosomes are called autosomal chromosomes . Complex Patterns of Inheritance • Sex-linked inheritance W+W+ WW WW+ Results not possible using Mendel… WW+ WW+ WW+ WW? Genes linked to X and Y Chromosomes Complex Patterns of Inheritance • Sex-linked traits: • Traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked traits. – Red-green color blindness – Hemophilia Complex Patterns of Inheritance X Chromosome Inactivation –Females only need one X chromosome to survive –Inside each cell of a female, one of the two X chromosomes are randomly deactivated (barr body) –Females Calico Cats random Complex Patterns of Inheritance • Environmental Factors: – Temperature, nutrition, light, etc… can effect the phenotype of an individual by changing the expression of the genes – Ex. Arctic Fox • Internal Factors: – Hormones regulate gene expression so a genotype may not express the same phenotype it different individuals – Ex. Peacocks Human Genetic Disease Presentations • Next Week: PPTs in groups of 4 Disease to Pick: – Select a genetic disease from the list today 1)Angelman Syndrome – NO LONGER THAN 10 MINUTES!!! 2) Cri du chat 3) Down Syndrome – Tell explain the following: 4) Neurofibromitosis 5) Prader-Wili • What causes the disease? Syndrome 6) Tay-Sachs Disease • What are the symptoms? 7) Turner Syndrome 8) Albinism • How common is the disease? 9) Canavan Disease • How can the disease be treated? 10) Haemochromatosis