* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Point Chapter 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
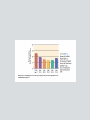
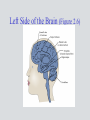
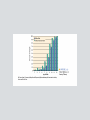
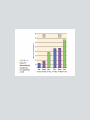
Chapter 2 Physical Development The prenatal development period is the time from conception to birth. The human zygote is the cell that is formed by the union of the sperm and ovum. The human zygote contains one set of 23 chromosomes from the mother and another set of 23 chromosomes from the father. Polygenetic Traits Human characteristics that result from the interplay of multiple genes. skin color height A trait not expressed reflects a recessive gene. A DNA Molecule (Figure 2.2) Males have an X and a Y chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes. Approximately 160 males are conceived for every 100 females. Sex-linked Characteristics Traits from recessive genes that are carried on the sex chromosome. Monozygotic twins come from the same fertilized egg and contain the same genetic instructions. Dizygotic twins develop from two different eggs. Down Syndrome • There is an extra twenty-first chromosome or a piece of one. • The disorder occurs 1 out of 1,000 live births. • Incidence has been linked to the age of the mother. • Children have a very characteristic appearance. Fragile-X Syndrome • One of the leading causes of mental retardation and developmental disabilities • Caused by a single gene • More common in males than females • Can be detected through genetic screening and DNA analysis Genotype The genes a person inherits from both parents for any particular trait. Phenotype The actual expression of inherited traits. The average period of human gestation is 38 weeks. Prenatal Development is divided into three major stages: • germinal period • embryonic period • fetal period Stages of Prenatal Development Teratogen Any environmental substance or disease that causes abnormal development of the fetus. The most common and direct cause of low birth weight is poor nutrition. The human brain is the largest among land mammals relative to body size. The human brain is not fully mature until early adulthood. The Central Nervous System • consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerve cells • controls almost every aspect of human functioning Left Side of the Brain (Figure 2.6) Half of the neurons produced during prenatal development die. Myelination • process whereby the neurons and dendrites become coated with a fatty substance called myelin • enables neural impulses to travel faster The idea that there is a “critical period” for brain development is an issue of debate. Though often thought true, there is no strong scientific evidence to categorize individual differences in learning styles according to left- and right-brain hemispheric specialization. (Hiscock & Kinbourne, 1987) Both cerebral hemispheres influence more aspects of cognitive functioning than was previously thought. Perceptual development involves the processing of sensory information by the brain. Habituation is the decrease in an infant’s response to a stimulus after repeated exposure to it. Fetuses can react to sound. Babies prefer sweet fluids to other tastes, and they dislike sour and bitter tastes. The sense of smell is present at birth. Newborns are responsive to touch. Attachment is the process by which infants form strong, affectional ties with their caregivers. Intermodal perception means that events or objects can be simultaneously perceived by multiple senses. Why does knowledge of children’s perceptual development have important implications for educators? Learning Disabilities • are not due to a lack of motivation or effort on the child’s part • is not due to poor teaching • is not due to a lack of intelligence • is not due to any temporary causes Possible Causes for Learning Disabilities • Heredity • Problems during pregnancy and birth • Incidents after birth Children with specific learning disabilities exhibit a wide range of academic learning problems. Potential Signs of Learning Disabilities, continued. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) • a commonly diagnosed behavior disorder • characterized by developmentally inappropriate levels of activity, concentration, distractibility and impulsivity. • more frequent in boys than in girls Many physical disabilities result from damage to the central nervous system. Children with low vision cannot read newsprint-size letters, even with corrective lenses. Children who are blind have either 20/200 vision or a limited field of vision. Traumatic Brain Injury • an acquired injury to the brain • either open or closed head injury • has significant impact on learning Children with deaf-blindness have dual sensory impairments. The degree of integration into the general classroom depends on a child’s level of cognitive development and communication ability. Autism • a neurological disorder • affects the functioning of the brain • more common in boys than girls By age 5 or 6, most children: • can copy simple geometric shapes • can manipulate buttons and zippers • may be able to tie their own shoes • can print the alphabet, letters in their name, and numbers 1 - 10 • may write large and not well organized on paper Girls tend to walk earlier than boys. By the early childhood years, boys outperform girls on most gross motor tasks. Children or adolescents with poor motor skills may avoid physical activities and become sedentary. Childhood obesity has been on the rise. As motor skills develop and children begin to spend more time away from the careful supervision of parents, the incidence of accidental injuries rises. Too may children are pushed into competitive sports before their motor skills have significantly matured. The average infant weighs approximately 7.5 pounds at birth. During the first year, an infant’s weight will triple. Cephalocaudal Development • Growth starts at the head and proceeds downward • The infant’s brain, neck, and trunk develop before the legs Proximal-distal Development • Development begins in the center and proceeds outward. • Organs develop before the arms or hands Physical growth slows down during the preschool and elementary years. The average American is growing taller today. Heredity plays an important role in determining a child’s shape and size. Nutrition is a core element of well-being throughout life. Sleep is a vital component of health and well-being. Puberty refers to the period in which a young person becomes capable of sexual reproduction. Ethnic differences in the onset of puberty are not well understood. Puberty is a dramatic period of physical development, second only to infancy. Puberty often leads to changes in adolescents’ self-image, self-confidence, family relations, moods, relations with the opposite sex, and many other behaviors. There is considerable individual variability in the onset of puberty. Early physical maturity in girls can have some positive consequences, but it also poses some risks. Young people today face a number of risks and challenges, including drug use, early sexual experimentation, and AIDS. FIGURE 2.13 Concerns of Children and Adolescents Today Source: Child Welfare League of America, 2005. • In 2001, almost half of the total number of enrollees in Medicaid were children under age 19. • In 2002, 425,493 babies were born to girls ages 15 to19, a birthrate of 43 per 1,000 girls. • In 2002, an estimated 2,209,000 children ages 12–17 were dependent on or abusing illicit drugs or alcohol. • Co-occurring mental health and substance abuse disorders are increasingly prevalent in youth; of youth treated for substance abuse disorders, 80–85% also have a mental health disorder. • In 2003, 1,687,814 children under age 18 were arrested; of these arrests, 25,531 were for violent crimes and 11,501 were for possession of a weapon. • A 2001 census showed that 104,413 children are housed in juvenile correction facilities in the United States. • In 2001, 1,890 children under age 20 committed suicide in the United States, a rate of 2.6 per 100,000 children. The percentage of young people who are overweight has more than doubled in the last 30 years. Childhood obesity has increased rapidly in the last 30 years. The eating disorder anorexia nervosa mainly affects adolescent girls between the ages of 14 and 18. Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder in which one goes on an eating binge and then vomits or uses laxatives as a way of purging the body. It is commonly believed that drug problems among young people are at an epidemic level in the United Stated. As a consequence of popular culture and society’s relaxed attitudes about sexuality, many researchers believe that young people are dealing with sexual issues at a younger age than ever before. Compared with adults, adolescents are at a higher risk for acquiring sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including HIV. The problem that has received the most attention is adolescent pregnancy. Schools, like other ecological contexts, support healthy development of children and adolescents and prevent risky behavior.