* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
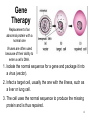
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning Adapted from the University of Utah Genetic Science Learning Center and The National Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health 1 Human Genome Project Goals: • To sequence & determine the exact order of the nucleotides (A,C,T,G) for ALL of the DNA in a human cell • To determine which sections of DNA represent the individual genes • To store this information in databases for analysis 2 How genes influence an individual’s response to drugs 3 Gene Therapy Replacement of an abnormal protein with a normal one Viruses are often used because of their ability to enter a cell’s DNA. 1. Isolate the normal sequence for a gene and package it into a virus (vector). 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung cell. 3. The cell uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and is thus repaired. 4 Problems with Gene Therapy • Short lived, so patients have to go through multiple rounds • Immune response to foreign invaders • Problems with the viruses • Very expensive • Multigene disorders: disorders like heart disease, high blood pressure, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes are caused by the combined effects of variations in many 5 diseases. Pedigree • A chart shows the relationships within a family of how a trait is passed from one generation to the next. Symbols used in pedigree charts In a marriage with five children, two daughters and three sons. The second son is affected by the condition. 6 Organizing the Pedigree Chart • To the right is a pedigree chart of a family showing four generations. A total of 20 individuals. • Generations are identified by Roman numerals. Individuals in each generation are identified by Arabic numerals numbered from the left. Therefore the affected individuals are II3, IV2 and IV3. 7 Genetically Modified Products • These are materials that the DNA has been altered within to express different traits. Golden Rice This rice has been modified to contain vitamin A and beta-carotene which are nutrients that many 3rd world country inhabitants won’t normally get from the foods they eat. Recombinant Bovine Growth Hormone This is a genetically engineered hormone that forces cows to make more milk than they normally would. 8 Genetically Modified Products Cont. Spider Silk Large scale production of artificial spider silk could lead to the development of stronger fibers for textiles, bandages for burn victims, and bulletproof vests. Insulin Mass production occurs with the help of bacteria. Edible Vaccine Bt Crops A naturally occurring soil bacteria that produces proteins active against certain insects. 9 What is Cloning? • Cloning is the creation of an organism that is the EXACT genetic copy of the mother • Identical twins are natural clones, they share 100% of their DNA 10 How do you clone an organism? 1. Remove the nucleus from an egg cell and a regular cell from a donor. 2. Fuse the enucleated cell with a regular cell (that still has its nucleus) by electric shock 3. The new fused cell begins dividing, just as a fertilized egg would. 4. The embryo is placed in the uterus of a surrogate mother and allowed to develop normally. 5. The surrogate mother gives birth to a genetic clone of the original egg cell donor donor! 11 Why Might We Want to Clone? • For medical purposes: – Cloning stem cells for researchstem cells may be used to repair damaged or diseased tissues and organs – Large populations of genetically engineered cloned animals may be able to produce drugs or proteins for medicine-process called “pharming” • Revive endangered or extinct species – Extinct not likely – Endangered possible but no success yet • Any reason to clone a human? – Help infertile couples have children? – “Replace” a deceased child? – Even if clones start out alike, there are many factors that occur after fertilization that lead to differences in appearance. In December ’01 the first domestic pet ever to be cloned was born – kitten named CC, next to her is her genetic donor. 12