* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brooker Chapter 2
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
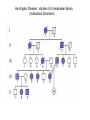
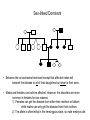
Human Genetics & Pedigrees November 29, 2007 BIO 184 Dr. Tom Peavy Human Genetic Traits Trait Hairline Shape Earlobe Form Ability to Roll Tongue Freckling Number of Digits Pigmentation Red Blood Cell Shape Ability to taste PTC Asparagus response Dominant Form widow’s peak present free present present more than 5 (polydactyly) present disk-shaped tastes bitter urine smells Recessive Form widow’s peak absent attached absent absent five absent (albinism) sickled (sickle cell anemia) no taste no smell Huntington Disease: studies of a Venezuelan family (Autosomal Dominant) Inheritance of Cystic Fibrosis (Autosomal Recessive) Sex-Linked Recessive • Males are more frequently affected than females. • Usually, the parents of affected children are normal, but the mother is a carrier. • Affected males, when they survive to reproductive age, cannot transmit the phenotype to their offspring unless they mate with a carrier or affected female. Their daughters, however, will all be carriers. Sex-linked Dominant • Behaves like an autosomal dominant except that affected males will transmit the disease to all of their daughters but never to their sons. • Males and females can both be affected. However, the disorders are more common in females for two reasons: 1) Females can get the disease from either their mothers or fathers while males can only get the disease from their mothers 2) The allele is often lethal in the hemizygous state, so male embryos die